Log in
Build Your Site
Web Designer vs Web Developer: What's the Difference?
What's the difference between a web designer and a web developer? You will find answers in this article.
A website serves as a crucial platform that connects a brand, web designers, web developers, and its users. As businesses increasingly rely on websites to establish their online presence, web design and web development have become popular career choices. However, many businesses and individuals still lack a clear understanding of the differences in roles, skills, and salaries between web designers and web developers, which can lead to a disconnect between job supply and demand in the market.
Imagine we’re sitting together at a Starbucks, having a friendly conversation. I look at you and ask, “Are you a business owner unsure whether to hire a web designer or a web developer?” Or perhaps, “Are you an individual struggling to choose between these two career paths?” You nod in agreement. Fortunately, you’re not alone—I understand your concerns. So, let’s dive into this article, where I’ll break down the key differences between a web designer and a web developer to help you make an informed decision.
What is Web Design?
Web design refers to the visual and interactive aspects of a website. It involves planning and creating the look, layout, information flow, and other aspects of a user interface, focusing on aesthetics, usability, and overall user experience (UX).
What is Web Development?
Web development is the process of building and supporting the technical aspects of a website. It involves coding, programming, and configuring the server and database to ensure that the website functions correctly and efficiently.
Key Differences between Web Designer and Web Developer

Roles: Web Designer vs Web Developer
What do web designers do?
Web designers are responsible for a website's user experience, color scheme, graphic design, and sometimes even content. In this role, they design the look and feel of a website to support its multiple uses.
What do web developers do?
Web developers are responsible for executing designs and bringing creative features to life. They are responsible for front-end development, coding of user-facing elements, and back-end configuration of servers and databases. They specialize in building websites from the ground up, utilizing their technical expertise and are proficient in complex coding techniques and high-level programming languages.
Once the site is live, web developers conduct post-launch testing, provide ongoing support, and ensure site maintenance to ensure your site is always up-to-date and optimized for a seamless user experience. They also ensure the site works on different browsers and mobile platforms and determine how to maintain its security.
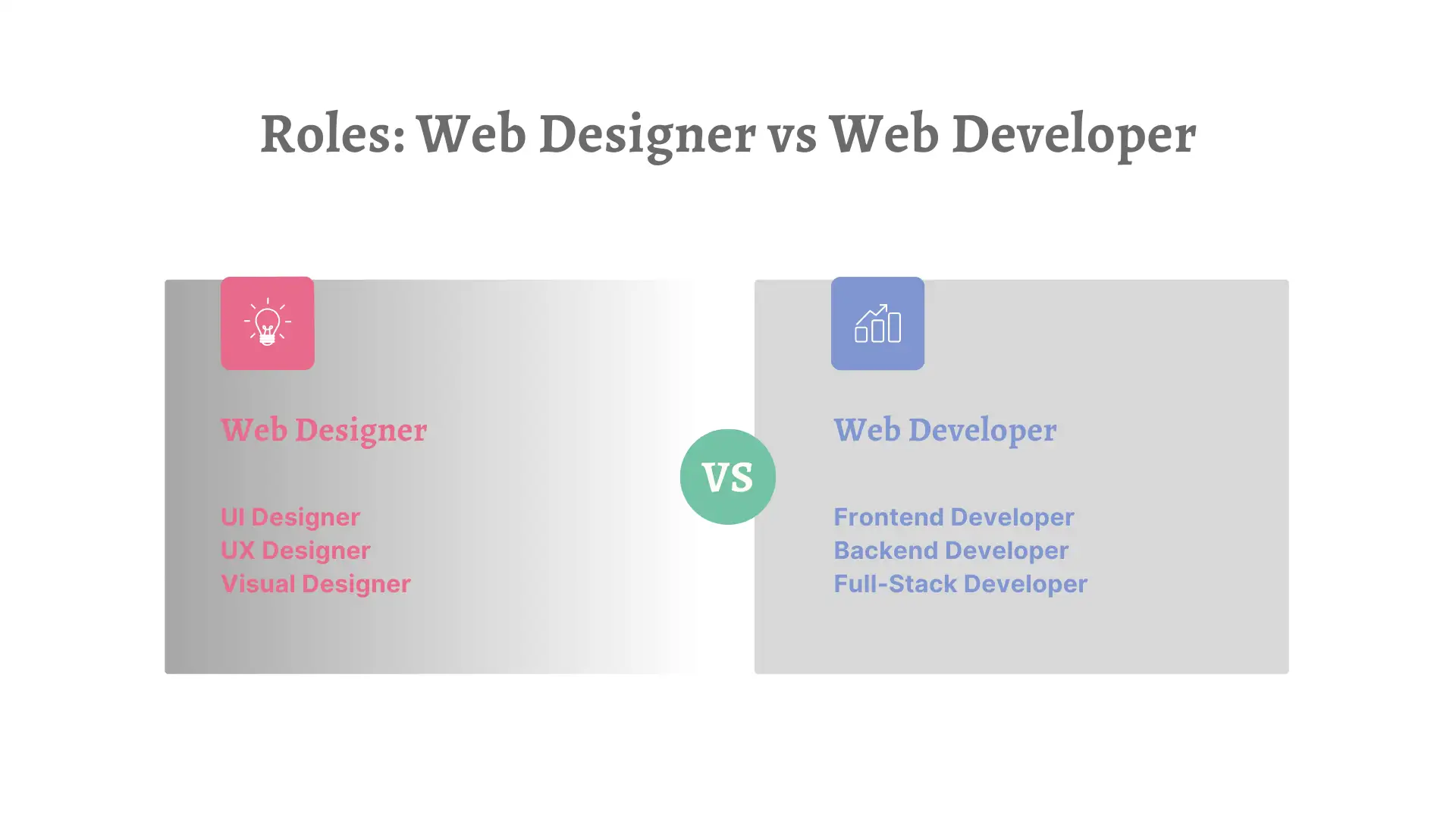
Common Types of Web Designers
-
User Interface (UI) Designer UI refers to the layout and design of a website. UI designers focus on the individual interactions that users have with the site, evaluating various features and predicting how users will perceive them as they navigate through the content. While UX designers make more data-driven decisions, UI designers are more concerned with the overall look and feel of the site.
-
User Experience (UX) Designer UX focuses on the interactive aspects of the website and encompasses the overall experience of using a product or service. UX can include many elements, such as the site map and the architecture of the content. Good user experience design goes beyond surface-level interaction and aesthetics. UX designers are responsible for ensuring that users have a pleasant experience while interacting with the site, using data collected about the target audience and user feedback to guide their decisions.
-
Visual Designer UX design is user-centered and emphasizes task flows and usage scenarios, while UI design prioritizes visual elements such as color, typography, and layout. The primary responsibility of a visual designer is to create visual elements that achieve specific goals, such as increasing product sales, enhancing brand awareness, or improving the user experience.
Common Types of Web Developers
-
Frontend Developer Frontend developers understand the user experience and strive to create visually appealing and engaging websites. They build websites using JavaScript, CSS, and HTML and use their design knowledge to create visually attractive user flows. They are proficient in various frontend frameworks and know how to optimize website performance.
-
Backend Developer In web development projects, backend developers ensure that the website functions correctly, processes large volumes of user data, and implements the site's business logic. They are responsible for managing the interactions between the server, application, and database, which form the foundation for delivering dynamic content and user-specific services. Backend developers write code that makes applications more secure, error-free, and efficient. They are proficient in multiple programming languages such as Python, Ruby, Java, and PHP, and are familiar with integrated application development frameworks like Django, and Laravel.
-
Full-Stack Developer Full-stack developers possess both frontend and backend development skills and can independently manage the entire process of website design, development, and deployment. They focus on user experience and interface design, ensuring that the website is both visually appealing and user-friendly. They handle the interactions between servers, databases, and applications, ensuring the website’s stability and security. Additionally, they are also concerned with website performance optimization to improve user satisfaction and overall site performance.
Skills: Web Designer vs Web Developer
Undoubtedly, different roles require different skills or tools to make a website perform well, though you may find that web designers and web developers share some common skills.
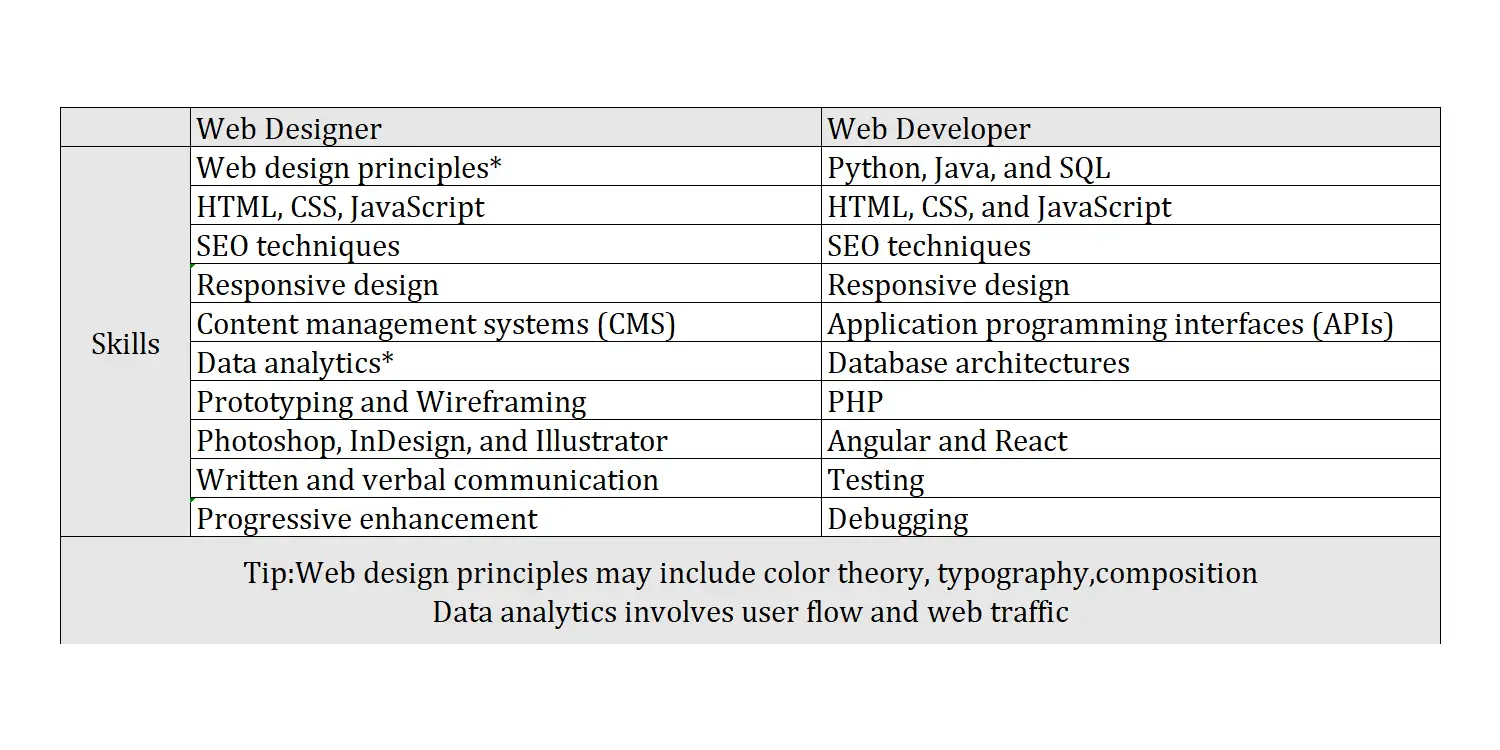
Definition
-
SEO: SEO refers to Search Engine Optimization. It is the practice of optimizing a website to improve its visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). This involves using various techniques such as keyword research, on-page optimization, content creation, and link building to attract organic traffic and ensure the site appears in relevant searches.
-
Prototyping and Wireframing: Prototyping is the process of creating a preliminary model or simulation of a product or website to test its design, functionality, and user interactions. Wireframing involves creating a visual blueprint or skeletal structure of a website or app. It represents the basic layout, content placement, and functionality, without focusing on design elements like colors and fonts.
-
Responsive Design: Responsive design is an approach to web design that allows websites to adapt to different screen sizes and orientations, providing an optimal user experience across devices such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
-
Progressive Enhancement: Progressive enhancement is a web development strategy that emphasizes delivering a basic, functional experience to all users, regardless of their browser capabilities, while adding enhanced features for those with more advanced browsers.
-
Angular and React: Developed by Facebook, React is a JavaScript library. Meanwhile, developed and maintained by Google, Angular is a TypeScript-based JavaScript framework.
-
PHP: PHP is an open-source, server-side scripting language primarily used for web development, and it is embedded within HTML code and executed on the server, allowing the generation of dynamic content.
The above skills and tools are important for their work but may not cover the full picture.
For web designers, mastering software skills such as Adobe Suite, coding tools, graphic editors, and wireframing/mockup tools can greatly enhance their ability to design extraordinary user interfaces. These skills enable them to create a smooth user experience by generating graphics that suit the website's target audience and purpose.
For web developers, using core web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, along with frameworks and libraries for both frontend and backend solutions, allows them to build dynamic and efficient websites that bring designs and creative features to life. Additionally, selecting an integrated development environment (IDE) can streamline the coding process and assist with debugging. Even after a website is published, web developers must continue monitoring its performance to ensure it functions as expected and delivers an optimal user experience.
Salaries: Web Designer vs Web Developer
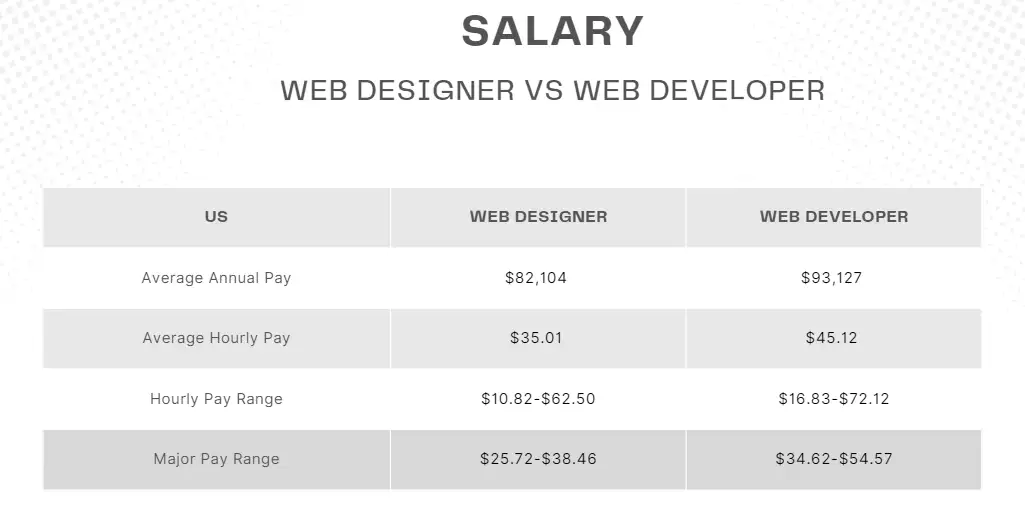
As of August 2024, the average annual salary for web designers in the United States is $82,104, according to Glassdoor. In comparison, web developers earn a higher average salary of $93,127 per year.
According to data from ZipRecruiter, as of September 22, 2024, the average hourly pay for web designers in the United States is $35.01. Hourly rates vary widely, ranging from as low as $10.82 to as high as $62.50. Most web designers' hourly wages fall between $25.72 and $38.46.
For web developers, the average hourly rate is higher, at $45.12. Hourly wages can range from $16.83 to $72.12, with most rates falling between $34.62 and $54.57 across the United States.
Many factors can influence the salaries of web designers and developers, including education, certifications, level of experience, job position, company size, location, and variations in job titles. For example, as of September 22, 2024, the average annual salary for a front-end developer in the United States is $110,412, while a full-stack developer earns an average of $117,880 per year.
Web Designer vs Web Developer: How to Choose?
Whether you are a business looking to hire the right professional or an individual deciding on a career path, understanding the key differences between web designers and web developers is crucial.
To Wrap up:
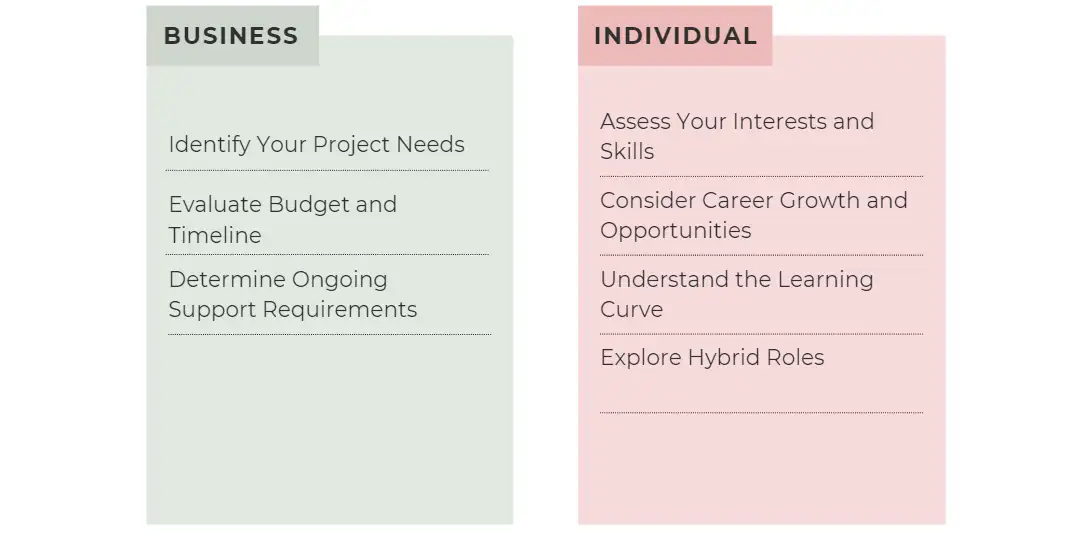
As a Business Employer
01.Identify Your Project Needs
Choose a Web Designer if your project requires a focus on aesthetics, branding, and user experience. A web designer will be responsible for creating visually appealing layouts, selecting color schemes, and ensuring that the site is user-friendly and aligned with your brand identity.
-
Choose a Web Developer if your project demands complex functionality, backend logic, or dynamic content. A web developer will build and maintain the technical foundation of the website, ensuring it performs well and functions seamlessly.
02.Evaluate Budget and Timeline
Hiring a web designer is often more cost-effective for projects primarily focused on design or redesign, while hiring a web developer may involve higher costs, especially if there’s a need for advanced programming and server management.
-
If your project requires both design and development, consider hiring a full-stack developer or forming a team that includes both a designer and a developer.
03.Determine Ongoing Support Requirements
A web designer can assist with continuous improvements in user interface and experience.
-
A web developer is necessary for updates involving backend features, performance optimization, or new functionality.
As an Individual Pursuing a Career Path:
01.Assess Your Interests and Skills
Choose Web Design if you have a passion for creativity, visual arts, and user experience. Web design might be a good fit if you enjoy working with graphic design tools, developing wireframes, and focusing on the aesthetics and interactivity of a website.
Choose Web Development if you are more inclined toward problem-solving, coding, and creating technical solutions. If you enjoy working with programming languages and building complex applications, web development may be the better path.
02.Consider Career Growth and Opportunities
Web Design: Roles in web design often lead to positions like UI/UX Designer, Creative Director, or Visual Designer. If you aspire to become a web designer, it’s essential to build a strong portfolio, gain hands-on experience through internships, and work on freelance or personal projects both during and after your education. This will showcase your skills and help you stand out in a competitive job market.
Web Development: Career paths in web development can lead to positions such as Frontend Developer, Backend Developer, Full-Stack Developer, or Software Engineer. At the beginning of your career, aim to secure an entry-level web developer position. Gaining experience in the field will deepen your understanding of the role and the industry, help you build professional connections, and provide opportunities for career advancement. As you develop your skills and expertise, you can move up the career ladder and take on more challenging and rewarding roles.
03.Understand the Learning Curve
Web design requires proficiency in design tools (e.g., Adobe XD), an understanding of design principles, and some basic coding skills (HTML/CSS).
Web development demands knowledge of programming languages (e.g., JavaScript, Python), frameworks (React, Angular), and backend technologies, which may involve a steeper learning curve.
04.Explore Hybrid Roles
If you’re interested in both visual design and coding, consider roles like Full-Stack Developer or UI/UX Designer. These hybrid positions combine design and development skills, giving you a well-rounded understanding of both creating the look of a website and building its functionality. This way, you can work on a wider range of projects and have a deeper insight into the whole web development process.
Conclusion
Web designers prioritize the visual appeal and usability of a website by focusing on layout, color schemes, and navigation to enhance the user experience. In contrast, web developers concentrate on the functionality of the site, ensuring it operates smoothly across different devices and browsers through technical implementation. Due to their distinct roles, designers and developers must master different skills and tools to contribute effectively to a website’s performance. However, despite their differences, they share a common goal: to create a visually appealing, user-friendly, and fully functional website. Additionally, their salaries are influenced by several factors, including level of experience, company size, and location.
Tip: If you want more information on web design and web development, you can click the following links. I hope they will help you.
Written by
Kimmy
Published on
Nov 10, 2024
Share article
Read more
Our latest blog
Webpages in a minute, powered by Wegic!
With Wegic, transform your needs into stunning, functional websites with advanced AI
Free trial with Wegic, build your site in a click!