Log in
Build Your Site
User-Centered Design: Everything You Need to Know in 2024
Discover everything you need to know about User-Centered Design in 2024. Learn its principles, processes, and examples from leading brands like Apple and Spotify. Explore future trends and how to make your designs more accessible and effective.

Have you ever thought about what makes some products connect with users while others miss the mark? The secret often lies in User-centered Design (UCD). User-centered Design prioritizes the needs and experiences of users throughout the design process, ensuring that products are not just functional but genuinely enjoyable to use.
In this blog, we'll explore what User-centered Design is, why it matters, and the key User-centered Design principles and processes that guide it. Whether you’re a designer, a developer, people are trying to redesign websites, or just curious about how great products are made, you’ll find valuable insights that can transform your approach to design in 2024.
What Is User-Centered Design?
The concept of User-centered Design originated in the 1980s. Designers gradually realized how important the user's real experience and feelings are when using products.
User-centered design is a design method. It takes user needs, expectations, and behaviors as core considerations. Whether it is a designer or a developer, their goal is to create products and services that can satisfy users. User-centered Design emphasizes that in the design process, designers should actively communicate with users, obtain feedback, and iterate to ensure that the final product can provide the best user experience.

Why User-Centered Design Important?
Today's market competition is fierce, products are diverse, and users have many choices. Therefore, if you want to stand out from many similar products, you should focus more on providing users with excellent user experience and leaving a deep first impression.
User satisfaction is a key indicator of product success. Studies have shown that 94% of first impressions are related to design, and poorly designed products often lead to user loss. According to a Forrester study, improving user experience can increase a company's revenue by up to 400%. This shows that a good user experience not only improves user satisfaction but also significantly improves the company's profitability.
When you prioritize user needs, you create products that are more intuitive and enjoyable to use. This leads to higher user satisfaction and loyalty, as users feel their preferences are being met. Satisfied users are more likely to recommend your product to others. This organic marketing can be invaluable, as personal recommendations often carry more weight than traditional advertising.
For businesses, a user-centered approach can lead to higher conversion rates. When users find a product easy to use and valuable, they’re more likely to make purchases or engage with services.
In summary, adopting a user-centered design approach can lead to products that not only meet user needs but also drive business success. Focus on your users and this helps you stay competitive in a constantly changing market.
4 Key User-Centered Design Principles
01.Empathy: Understanding User Needs and Contexts
Empathy in UCD involves putting yourself in the users' shoes to understand their feelings, thoughts, and experiences. Imagine that you are a user, and you can ask yourself: what do you want or expect most when you use this product or service? What problem do you hope it can solve for you?
To get to know more effective and useful information, you can collect real data through user surveys, interviews, and observations. You can try to create user personas to represent different user segments and their needs. User personas help you understand the background, habits, and pain points of the target users. It also helps you make decisions that are more in line with the actual needs of users when designing.
By deeply understanding users, you can create solutions that truly resonate, addressing pain points and enhancing overall satisfaction.
02.Users Involvement: Getting Users Involved in the Design
User involvement is another important principle you need to follow. You can involve your target users from the very beginning and at various stages of the design process. From your prototype to your final testing and implementation, you can always invite users to join in your design projects. They are important sources to give you some important feedback. Especially when you start your prototype, their feedback can lead to valuable insights that help refine features before full development.
By doing so, users will foster a sense of ownership and trust in the product, leading to better alignment with user needs.
03.Iteratation: Refining Designs Based on Feedback
Design is a process of continuous improvement. User-centered design emphasizes collecting feedback and iteration. The initial design may not be perfect or could not fully meet user needs, and repeated testing and modification can ensure that the final product is more in line with user expectations.
As a designer, you can establish a cycle of testing, feedback, and refinement. You can also use methods like A/B testing and usability testing to gather insights on what works and what doesn’t. Iterating based on real user feedback allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to new challenges. So, just be open and listen to the user's voice and constantly improve the product on this basis.
04.Accessibility: Making Your Design Accessible to Everyone
Accessibility ensures that all users, including those with disabilities or the elderly, can use the product normally. With more people advocating equal access to digital products, we must design with everyone in mind. According to the World Health Organization, about 15% of the world's population faces some degree of disability, so it is crucial to consider accessibility when designing.
Designers should follow barrier-free design principles, such as providing adequate contrast, and using readable fonts, and should consider how different audiences will conduct their products.
What's more, you can conduct usability testing with users who have different abilities to identify potential barriers. Tools like screen readers and keyboard navigation should be considered in the design process.
Making products accessible not only broadens your user base but also enhances the overall user experience for everyone. It’s a win-win situation that can lead to greater user loyalty and satisfaction.

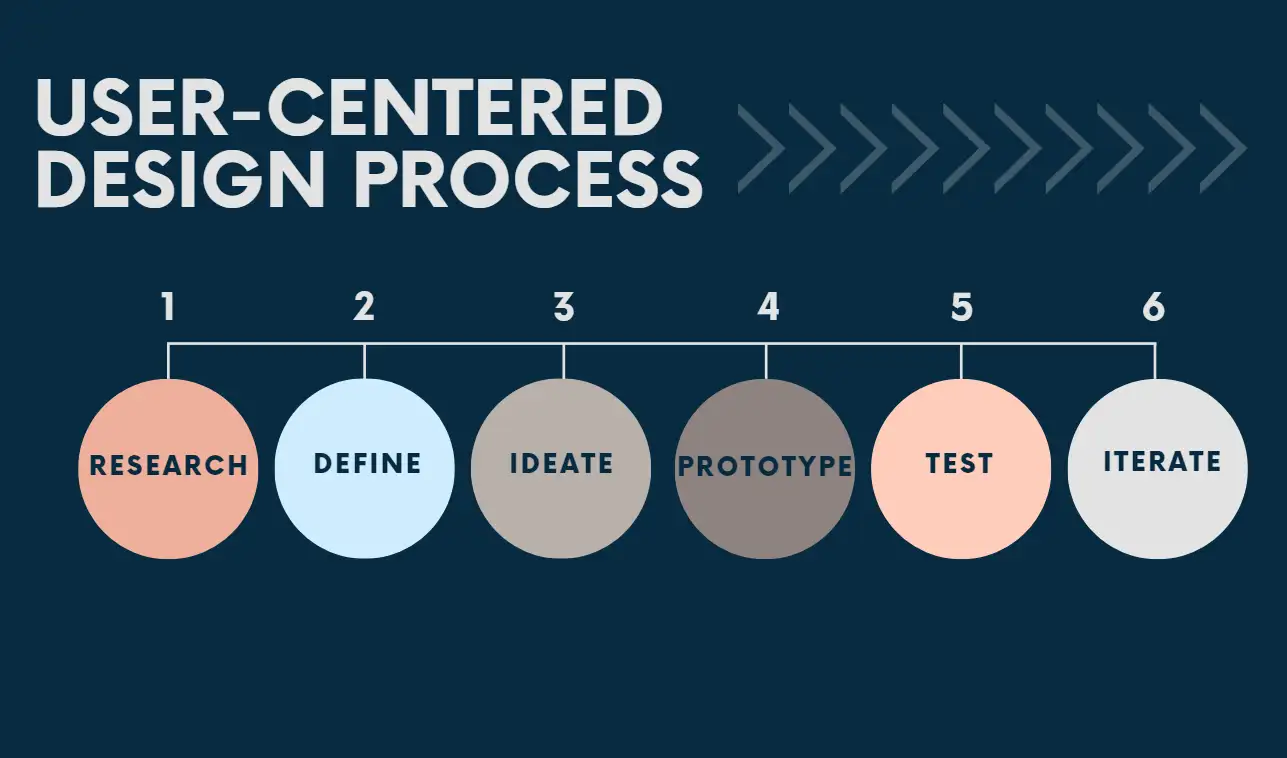
The User-Centered Design Process
The User-Centered Design (UCD) process puts real users at the heart of the design, making sure their needs and feedback shape the final product. Let’s break it down step by step!
#1 Research: Get to Know Your Users
First things, before you start designing anything, you need to understand who your users are. You can do this by talking to them. There are a lot of ways, like conducting interviews, sending out surveys, or even watching how they use similar products. This helps you gather insights about their preferences, challenges, and goals.
#2 Define: Pinpoint the Problem
Now that you have some information, it’s time to focus on what you’ve learned. What are the key issues your users face? Write down clear problem statements that reflect their needs. This is like your design compass. Everything you create should guide users towards solving these problems.
#3 Ideate: Let Your Ideas Flow
Now you can prepare a blank board and start brainstorming. No idea is too crazy at this stage. You can sketch out rough concepts or jot down all your thoughts. The goal is to generate a variety of solutions that might work for your users. These potential design solutions can be further refined.
#4 Prototype: Bring Your Ideas to Life
Once you have some solid ideas, it’s time to create prototypes. There are two types of prototypes, low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes. Think of prototypes as rough drafts for your product. They can be anything from paper sketches to digital mockups. Choosing which one mainly depends on your needs. The key here is to make something tangible that you can show to users.
#5 Test: Get Feedback from Real Users
Share your prototypes with real users and gather their feedback. Observe how they interact with your designs to identify areas for improvement. This is important because effective feedback can help you improve your designs.
#6 Iterate: Improve Based on Feedback
After testing, you’ll likely discover some areas for improvement. Don’t worry if things don’t go perfectly—this is all part of the process! You can analyze testing results, identify pain points, and make necessary adjustments. Repeat the prototyping and testing stages as needed. Go through the prototyping and testing stages to enhance the user experience before final implementation.
User-Centered Design Examples
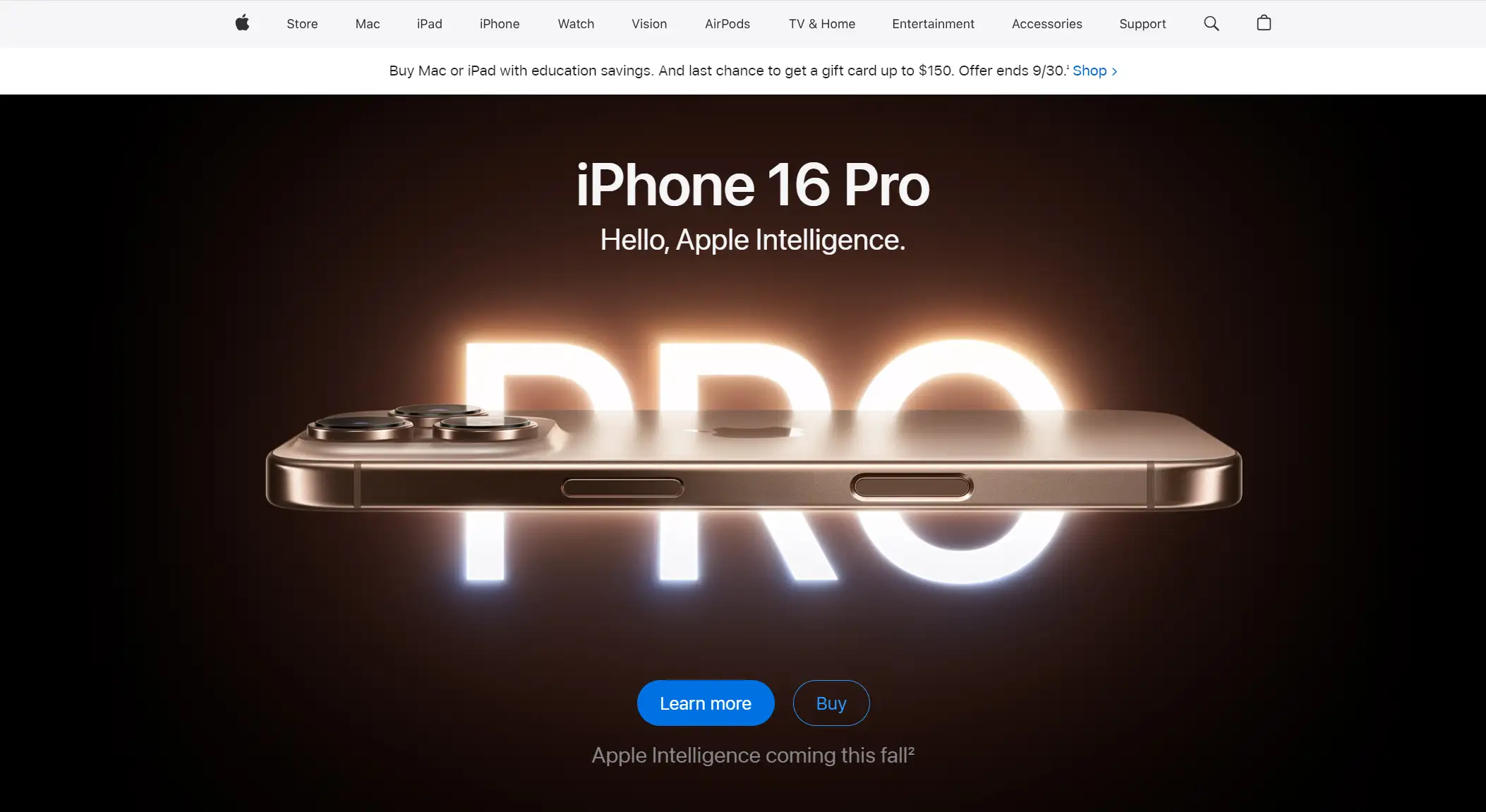
Apple iPhone
What they do: The iPhone is a prime example of user-centered design, focusing on intuitive use and seamless functionality.
Apple conducted extensive market research to understand user frustrations with existing smartphones, such as complicated interfaces and poor usability.
The iPhone introduced a simple touch interface with a clean layout, making it accessible even for those unfamiliar with technology. Features like pinch-to-zoom and swipe gestures were revolutionary and intuitive.
The sleek design combined form and function, emphasizing usability without sacrificing style.
Outcomes: The iPhone’s focus on user experience and elegant design not only changed the smartphone industry but also created a loyal customer base, making Apple one of the most valuable companies in the world.
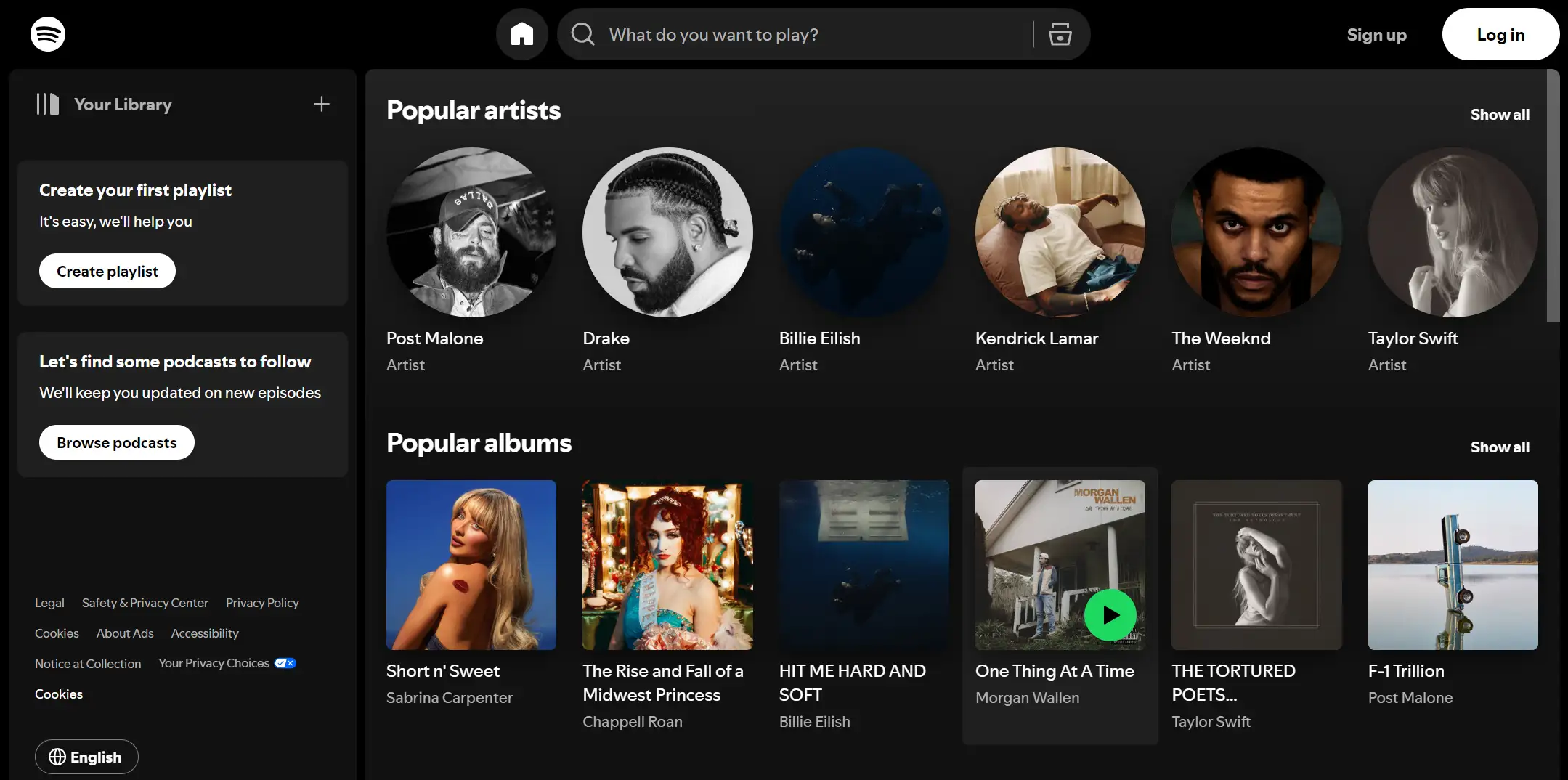
Spotify
Spotify revolutionized music streaming by centering its design around user preferences and listening habits.
What they do: Spotify uses algorithms to create personalized playlists, such as "Discover Weekly," which curates new music based on users' listening history. This feature makes users feel understood and keeps them engaged.
The app features an intuitive layout, making it easy for users to navigate playlists, and albums, and discover new music. The search function is simple and effective, allowing quick access to favorite tracks.
Outcome: By focusing on personalization and user engagement, Spotify has attracted millions of users worldwide, establishing itself as a leader in the music streaming industry.
Future Trends in User-Centered Design
Nowadays, emerging technologies like artificial intelligence are set to reshape User-Centered Design in exciting ways. We know AI can analyze vast amounts of user data, helping us understand what users truly want. This means that when designing a product, you can create personalized experiences that feel tailor-made for each individual. If you think about it, this personalization can significantly enhance user satisfaction and engagement, making users feel more connected to the product.
Furthermore, with technology evolving, we must anticipate changing user behaviors and preferences. Rapid advancements mean that what users expect today may not be the same tomorrow. If you keep an eye on trends and gather regular feedback, you can adapt your designs accordingly. Agile design methodologies, which focus on quick testing and iteration, can help you stay ahead of the curve. In my opinion, this flexibility is key to maintaining relevance in a fast-paced market. By being open to change and actively listening to users, you can create products that not only meet current needs but also anticipate future demands.
Wrapping Up
In this blog, we have delved into user-centered design, including its definition, importance, main principles, and how to conduct a user-centered design process.
In a world where user expectations are constantly evolving, embracing User-Centered Design is more crucial than ever. By understanding user needs, involving them in the design process, and iterating based on their feedback, you can create products that not only meet but exceed user expectations.
As we look to the future, staying adaptable and aware of emerging trends will keep your designs relevant and impactful. So, are you ready to put your users at the heart of your design process? By prioritizing User-centered design, you can craft experiences that truly resonate and stand out in a competitive landscape.
FAQs
What are the key differences between UCD and traditional design approaches?
User-centered design (UCD) focuses on understanding users' needs and involving them throughout the design process, ensuring the final product meets their expectations. In contrast, traditional design often relies on assumptions and expert opinions, with less emphasis on user feedback. This can lead to products that may look good but don’t necessarily serve users well.
How can I get started with UCD in my projects?
To start with UCD, begin by researching your target users through interviews or surveys to understand their needs. Create user personas to guide your design. Involve users in brainstorming and testing your prototypes, gathering their feedback to refine your design. Stay flexible and open to changes based on what you learn.
What tools and resources are available for user-centered design?
For UCD, consider using tools like SurveyMonkey for research, Xtensio for creating user personas, and Figma or Adobe XD for prototyping. For usability testing, platforms like UserTesting are helpful. Additionally, look for online courses and books on user experience to deepen your understanding.
Read More
Written by
Kimmy
Published on
Jan 25, 2025
Share article
Read more
Our latest blog
Webpages in a minute, powered by Wegic!
With Wegic, transform your needs into stunning, functional websites with advanced AI
Free trial with Wegic, build your site in a click!