Log in
Build Your Site
How to Scan Website Vulnerability: 6 Best Tools in 2025
Worried about website security? Discover 6 top tools to scan vulnerabilities. Protect your site today—click to learn more and secure your online presence!
The Internet can disrupt company operations, hinder profits, and compromise the private data of millions through phishing attacks, leading to significant losses for businesses, customers, and entire industries. Have you scanned your website, computer system, and network for security vulnerabilities since launching your company? If not, it’s crucial to prioritize this task.
If you've already begun checking for website vulnerabilities but found manual inspections to be too time-consuming and costly, you may be wondering what tools can help automate the process. To efficiently identify potential vulnerabilities and safeguard your company’s digital environment, this article is here to assist you.
We provide a comprehensive overview of website vulnerability scanning, including common types of vulnerabilities, popular scanning tools, and more. We hope you find the answers you’re looking for.

Why is it Important to Scan Website Vulnerability
You may be familiar with notable cases of cyberattacks. For instance, in 2023, the Real Estate Wealth Network experienced a data breach resulting from a malicious cyberattack, leaking an astonishing 1.5 billion records. That same year, MOVEit Transfer, a widely used secure file transfer software, suffered a major breach, exposing sensitive data for over 94 million users and more than 2,500 enterprises, with losses exceeding $10 billion.

Vulnerability scanning, also known as vulnerability assessment, is the process of evaluating networks or IT assets to identify security weaknesses. This method is one of the most effective ways to detect known vulnerabilities and spot potential weaknesses in application security. Organizations frequently use website vulnerability scanners to detect and report vulnerabilities that may impact their systems, enabling proactive mitigation and protection of digital assets.
Website vulnerability scanning is essential for organizations of all sizes, as it helps ensure the security of company networks, systems, and applications. By regularly scanning for vulnerabilities, organizations can strengthen their existing security measures, identify areas for improvement, and reduce the risk of cyberattacks. Here are four key reasons why vulnerability scanning is crucial:
-
Identify Weaknesses: Proactively addressing vulnerabilities helps mitigate risks before they escalate. Using specialized tools to detect security gaps across websites, applications, and networks in advance can prevent cyberattacks and data leaks caused by hackers or other sources.
-
Compliance Management: Adhering to security standards and regulations, such as NIST, PCI-DSS, and DSS, helps organizations meet legal requirements and avoid potential liabilities. Vulnerability scanning plays a significant role in achieving and maintaining these compliance standards.
-
Risk Management: By generating detailed reports, vulnerability scanners provide insights into the security status of various aspects of a website, identifying vulnerabilities and assessing their severity. This enables organizations to prioritize threats, allocate resources effectively, and support customers in managing their risks.
-
Save Time and Cost: Vulnerability scanning, including both automated and manual scanning, helps reduce time and labor. Automated scans offer continuous monitoring, saving time and ensuring security remains a consistent priority.
In summary, website vulnerability scanners are invaluable tools for identifying, prioritizing, and addressing security issues. They contribute to a more robust and resilient digital infrastructure, empowering organizations to protect sensitive data and maintain system integrity effectively.
What You Should Know Before Scanning Website Vulnerabilities
When a network is compromised, unauthorized access can lead to data theft, damage to critical information, and even system crashes or operational disruptions.
Common Web Vulnerabilities
-
Open Redirection: Also known as URL redirection vulnerability, this issue allows attackers to exploit a website's normal redirection mechanism to redirect users to a malicious URL specified by the attacker. This vulnerability can exist in both web applications and mobile apps.
-
Reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): In this type of attack, the attacker inserts malicious scripts or codes into a web page. When a user visits the page, the embedded script is executed, enabling the attacker to carry out malicious actions against the user. Automated scanners often send test strings containing HTML tags in response to identify these vulnerabilities.
-
Command Injection: This web security vulnerability enables attackers to execute arbitrary operating system commands on the server, potentially exposing sensitive data or taking control of the system. PHP command injection is a common vulnerability in PHP applications.
-
SQL Injection: This security vulnerability occurs at the application and database layers when attackers insert malicious SQL queries into an application to compromise the database. Basic payloads can sometimes be used to trigger recognizable error messages, aiding in detection.
-
Directory Listing: This is a configuration issue in web services that allows access to an exposed directory, revealing a list of files within it. While this behavior isn't inherently an attack, it can lead to the leakage of sensitive information in certain cases.
Key Systems for Website Vulnerability Scanning
Before scanning for website vulnerabilities, it's essential to understand two key systems:
-
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS): CVSS is a standardized system for assessing the severity of security vulnerabilities in computer systems. Scores range from 0 to 10, with 10 indicating the most severe vulnerabilities.
-
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE): The CVE system provides a reference method for known information security vulnerabilities and exposures. It enables IT professionals to prioritize and address these issues effectively.

How to Scan Website Vulnerability: 6 Best Tools in 2025
Vulnerability scanners are automated tools designed to scan web applications for security risks, running thousands of tests to identify common vulnerabilities. These tools help identify security issues on your website, enabling you to address them and improve your overall vulnerability management strategy. Here, we've picked six of the best website vulnerability scanners to help you efficiently scan and secure your website in 2025.
1#CloudSploit
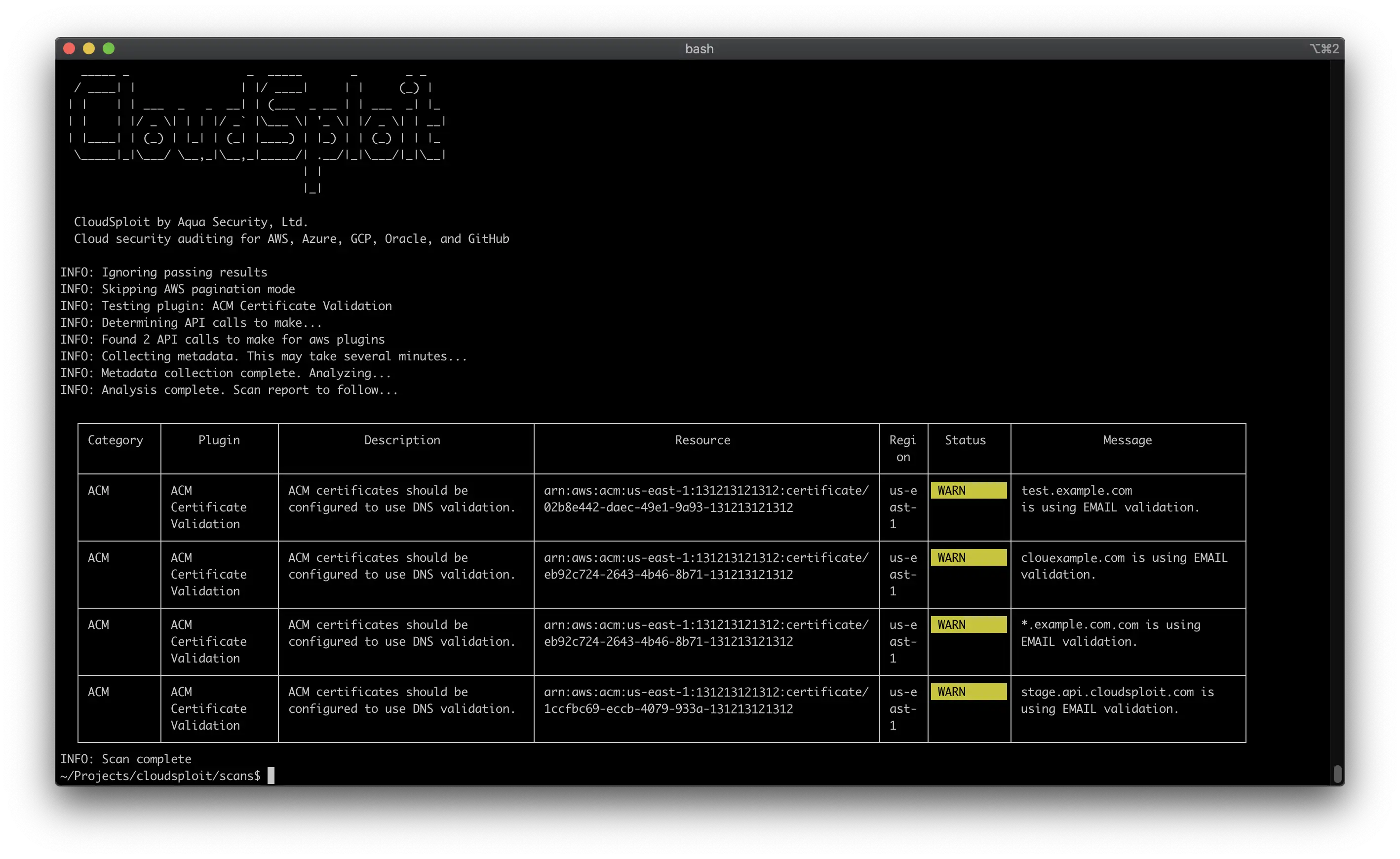
CloudSploit, developed by Aqua Security, is an open-source Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tool designed to detect security risks across various cloud platforms, including AWS, Azure, GCP, OCI, and GitHub. It identifies both known vulnerabilities and common misconfigurations in cloud and container deployments. The tool operates in two main stages.
First, it collects metadata from cloud accounts via APIs, which it then analyzes to identify potential risks and misconfigurations.
Second, it proceeds to the “scan” phase, where it uses the metadata to detect specific misconfigurations, risks, and other security issues, providing a comprehensive output of findings.
CloudSploit can be deployed as a self-hosted solution or through Aqua's managed service, Aqua Wave. It supports customizable CLI options, and compliance-focused scanning, and exports results in formats like JSON and CSV to facilitate integration into broader security workflows.
Pricing: CloudSploit is a website vulnerability scanner online free for everyone. The frequent updates from Aqua Security keep it robust and current.
2#GFI LanGuard
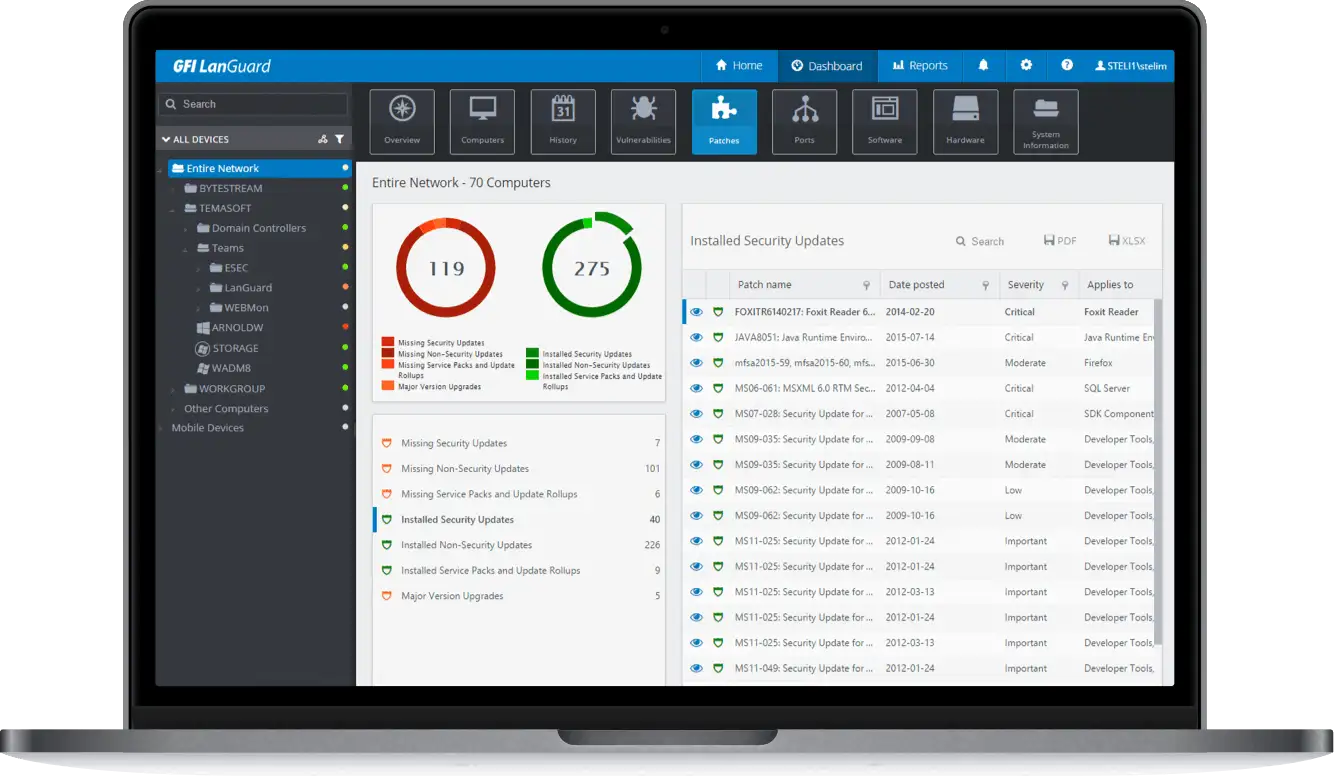
GFI LanGuard is a comprehensive network security and patch management tool. It offers scanning, patching, and compliance solutions.
GFI LanGuard supports centralized patch deployment, either directly or via agent-based installations, to reduce server load. In addition to patching for Windows, macOS, Linux, etc., it can audit network security for vulnerabilities across web browsers and third-party applications.
It includes a central dashboard for vulnerability assessments, patch management, and network auditing, compatible with various operating systems and applications.
Pricing: GFI LanGuard's pricing starts at $32 per user per month (minimum 10 users), and licensing is based on the number of nodes, with subscription options available for 12, 24, or 36 months.
3#Nmap
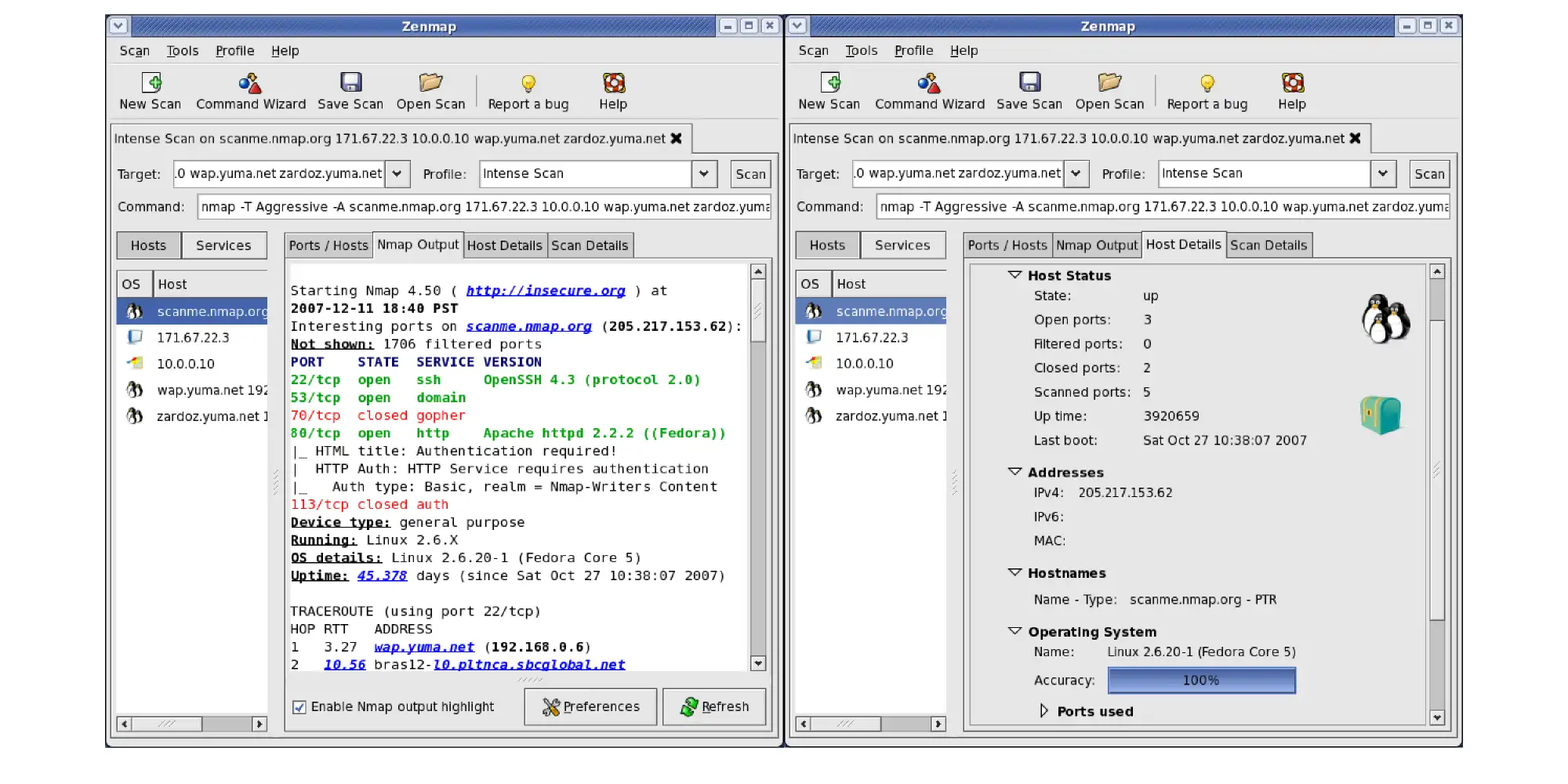
Nmap, short for "Network Mapper," is an open-source tool widely used to scan website vulnerabilities. It is known for its speed and extensive scanning capabilities.
Nmap can analyze anything from a single host to large networks with hundreds of thousands of devices. Nmap is popular among security experts and hackers, serving purposes like network inventory, service upgrade scheduling, and host monitoring. It provides detailed information on host availability, open ports, OS versions, firewall types, and more.
Nmap runs on major operating systems, with official binaries available for Linux, Windows, and macOS. The tool even appeared in The Matrix Reloadedand integrates with security tools like Nessus and OpenVAS. Additionally, Nmap offers over 500 community-developed scripts, enhancing its abilities for network discovery and vulnerability assessment.
Pricing: Nmap is one of the vulnerability scanning tools free to download, with open-source licensing allowing modification and redistribution. Its goal is to support internet security by providing administrators, auditors, and hackers with advanced tools for exploring networks.
4#OpenVAS
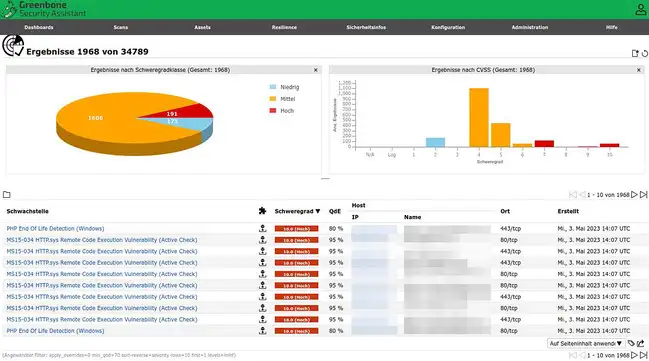
source: bsi
OpenVAS, developed by Greenbone, is an open-source website vulnerability scanning and management tool with a large user community, cybersecurity certification resources, and compliance reporting. It offers extensive customization to meet specific security needs, free from commercial license restrictions.
OpenVas's key features include both authenticated and unauthenticated testing, scalability for large-scale scans, and a specialized programming language for detecting vulnerabilities. OpenVAS scans a wide range of devices, including endpoints, servers, and cloud deployments, identifying CVEs. The paid version supports additional device scanning.
OpenVAS maintains a comprehensive, regularly updated Network Vulnerability Testing (NVT) database. Its modular design allows for feature additions or modifications, and it supports integration with other open-source tools via APIs, enabling custom connections to proprietary systems.
Pricing: The open-source community version provides a website security check online free to everyone. For advanced scanning, including IoT devices and additional support, users can upgrade to the Enterprise Edition.
5#OSV-Scanner
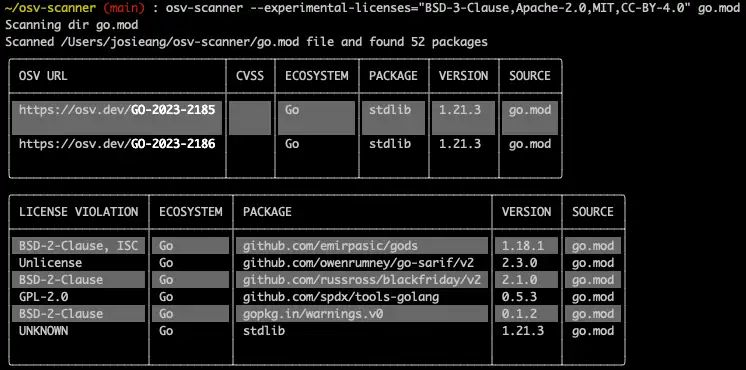
OSV-Scanner, developed by Google, is an open-source tool designed as a front-end for the OSV (Open Source Vulnerabilities) database. It links a project’s dependency list to potential vulnerabilities, allowing developers to identify and resolve security issues within dependencies.
OSV-Scanner’s open-source nature ensures each advisory is community-sourced and trusted (e.g., from RustSec), with users also able to suggest improvements. Its standardized format enables quick matching of vulnerabilities with software packages, offering high-quality software composition analysis (SCA) for securing open-source projects.
It extracts vulnerability data from multiple sources, including Debian, PyPI, RubyGems, Linux, OSS-Fuzz, Packagist, NuGet, Maven, and npm, and supports languages such as C/C++, Dart, Elixir, Go, Java, JavaScript, PHP, Python, R, Ruby, and Rust. Its flexible deployment enables API, scriptable, and GitHub integrations, making it ideal for DevSecOps automation.
Pricing: OSV-Scanner is free and available to the developer community.
6#ZAP
Zed Attack Proxy (ZAP), a dynamic application security testing (DAST) tool released under the Apache License, is popular among open-source vulnerability scanners for its flexibility and ease of use. It offers both automated and manual testing, supporting all major operating systems and Docker.
ZAP performs extensive network vulnerability scans, allowing developers to automatically detect security issues as they develop and test web applications. DevSecOps integration is available through API and Docker, streamlining automation and tool integration.
Pricing: ZAP is free. It also has optional support packages: bronze ($10,000/year) and silver ($20,000/year), which include direct email or video support and quicker response times.
Final Thought
In today's digital landscape, hackers continuously seek vulnerabilities in endpoint devices and web applications, exploiting misconfigurations, missing patches, and more to penetrate IT infrastructures. Cybersecurity, therefore, is crucial to safeguarding our online lives. Ensuring your website's data is secure begins with vulnerability scanning.
When choosing a website vulnerability scanner, it's essential to consider key features, usability, pros and cons, and cost.
For a seamless alternative, consider Wegic—our AI-powered website builder. With Wegic, you can chat with our AI assistant, Kimmy, to create a secure site in seconds. Enjoy a free trial with 70 credits, no coding needed, and easy customization. Enhance your cybersecurity effortlessly with Wegic while ensuring a robust, hacker-resistant website.
Written by
Kimmy
Published on
Mar 18, 2025
Share article
Read more
Our latest blog
Webpages in a minute, powered by Wegic!
With Wegic, transform your needs into stunning, functional websites with advanced AI
Free trial with Wegic, build your site in a click!