Log in
Build Your Site
What Is a Fully Qualified Domain Name? A Beginner's Guide
Read the articke, and learn the structure, function, and best practices for using a fully qualified domain name in websites, SEO, and digital infrastructure.
A fully qualified domain name (FQDN) is more than just a technical string. It's the cornerstone of how websites, apps, and services are located and identified online. For developers, website owners, marketers, and IT teams, understanding the FQDN meaning and structure is essential to building secure, optimized, and scalable digital environments. But,How to create a website with a domain name?

In this guide, we'll walk you through everything you need to know about FQDN—from what they are and how they work to common mistakes and best practices for implementation. You'll also discover how to simplify the FQDN setup using Wegic, the AI-powered website builder that automates everything from domain configuration to going live—no technical background required.
What Is a Fully Qualified Domain Name
A FQDN is the complete version of a domain name that uniquely identifies a specific host on the Internet. It includes every level of the domain hierarchy, from the hostname and subdomain to the top-level domain (TLD) and the root. Unlike a basic domain like example.com, an FQDN includes the hostname, subdomain, registered domain, top-level domain (TLD), and ends with a root dot (.), making it a precise and absolute reference.
For example:
-
A simple domain might be: example.com
-
A fully qualified version would be: www.example.com.
That trailing dot at the end represents the root domain. While it's usually hidden in browsers, it's crucial in backend systems as it signals that the domain is absolute and fully specified. Because nothing more can be added to it, it's referred to as a fully qualified domain name.
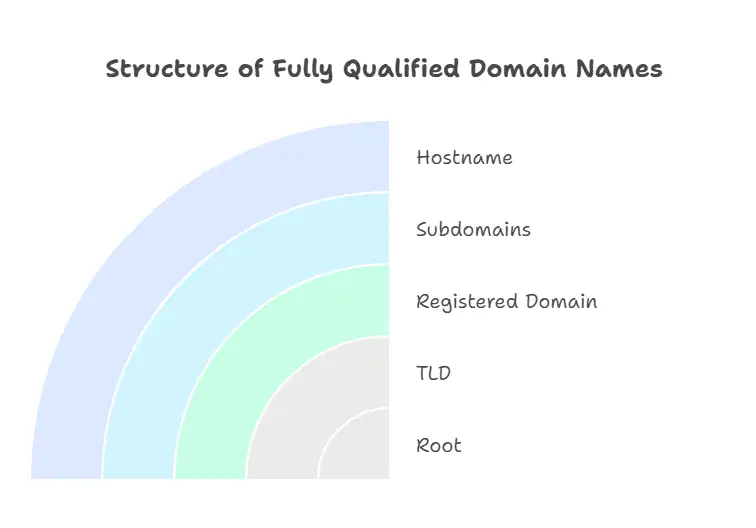
The Structure of Fully Qualified Domain Names
The structure of fully qualified domain names is related to domain choosing. A FQDN consists of multiple hierarchical layers, each representing a level within the Domain Name System (DNS). To better understand the domain name structure, consider this example: www.blog.store.example.com. Every part of this domain plays a specific role in DNS resolution.
1.Subdomains
In this case, "blog" and "store" are subdomains created under the main registered domain, example.com. They often represent different sections or services of a website.
2.Hostname
"www" is commonly used as the hostname, though it could also be other labels like "mail," "api," or "app," depending on the specific server or application being referenced.
3.Registered Domain Name
This refers to example.com, which is the core domain you register through an ICANN-accredited registrar. It's your primary, controllable web address.
4.Top-Level Domain (TLD)
This is the last segment, such as .com, .org, or .io, representing the highest level in the domain name hierarchy. Different TLDs can imply various purposes, regions, or industries.
5.Root
At the very end of an FQDN is the root, represented by a trailing dot (.). While this is typically hidden in browser address bars, it plays a critical role in DNS systems by marking the absolute end of the domain path.
So, a complete domain name structure would be written as:
[hostname].[subdomain].[registered domain].[TLD]. (Yes, including the final dot.)
The Importance of Fully Qualified Domain Names
A Fully Qualified Domain Name serves as the unique and absolute address of your website on the internet. Without it, the Domain Name System (DNS) can't correctly route users to your server's IP address. It's essential for a wide range of critical services in web infrastructure.
For example, SSL certificates must be issued for a specific FQDN—without this, browsers will flag your site as "not secure." Search engines rely on Fully Qualified Domain Names to index your pages correctly, which directly impacts your SEO performance. Email systems, including protocols like MX, SPF, and DKIM, require precise FQDN settings to ensure secure and accurate mail delivery.
If you're running a site with multiple subdomains, regional pages, or language versions, each one needs its own unique FQDN to function properly. In short, whether you're setting up basic DNS, securing your site with HTTPS, or launching a multi-site digital strategy, a FQDN is the technical backbone that makes everything work.
One of the most overlooked steps in website creation is planning your domain name structure. Ignoring this can lead to long-term problems like failed SSL setups, SEO performance issues, and even site migration headaches.
1.It's the foundation of effective SEO
Search engines use FQDNs to understand how your site is organized. A clear and consistent domain structure helps crawlers determine page relationships, improves how efficiently your content gets indexed, and increases domain authority.
2.It reinforces brand consistency
Decisions like whether to use a subdomain or a folder path, include "www," or set up proper 301 redirects all impact how professional and unified your brand appears online. For example:
www.brand.com vs brand.com
store.brand.com vs brand.com/store
3.It's essential for third-party integrations
CDNs, SSL certificates, and services like Cloudflare, Google Workspace, or Stripe all require a correctly configured FQDN. Using temporary or poorly structured domains often results in setup errors or service rejections.
4.It streamlines smart platform integration
If you're using an AI-powered website builder like Wegic, the platform automatically assigns and configures your FQDN, handles DNS binding, and publishes your site—all without manual intervention. That means faster launches with fewer technical steps.
The Critical Role of Fully Qualified Domain Names in Network Security
In modern networking, a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) is far more than just a routing label—it's a foundational element of digital identity and access control. Whether you're encrypting web traffic, verifying email authenticity, or enforcing security policies, the FQDN plays a pivotal role in keeping systems secure.
1.SSL/TLS Certificates Depend on FQDNs
For any website to run over HTTPS, it must present a valid SSL/TLS certificate that's specifically issued for its FQDN. For example, www.example.com and example.com are treated as different entities, best domain extensions—if you attempt to secure one but serve the other, users will be greeted with a browser warning like "connection not secure" or "certificate not trusted." This is why wildcard or multi-domain certificates are sometimes necessary for sites with multiple subdomains.
2.Secure Email Protocols Require Precise FQDN Configuration
Email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC rely heavily on properly configured FQDNs. SPF verifies the sending server's IP against an authorized domain; DKIM signs messages using a domain-linked cryptographic key; DMARC builds on both and provides visibility into unauthorized sending activity. If your FQDN setup is incorrect or incomplete, your emails may be flagged as spam or rejected altogether, damaging both deliverability and domain reputation.
3.FQDNs Power Zero Trust and Firewall-Based Access Control
As Zero Trust architecture becomes the norm, domain-based access control has emerged as a key security mechanism. Firewalls, proxies, and microservices increasingly rely on FQDNs to define rules around trusted communication. Instead of simply allowing traffic based on IP, modern systems use domain identifiers to grant or deny access, ensuring that only verified endpoints can interact across your infrastructure.
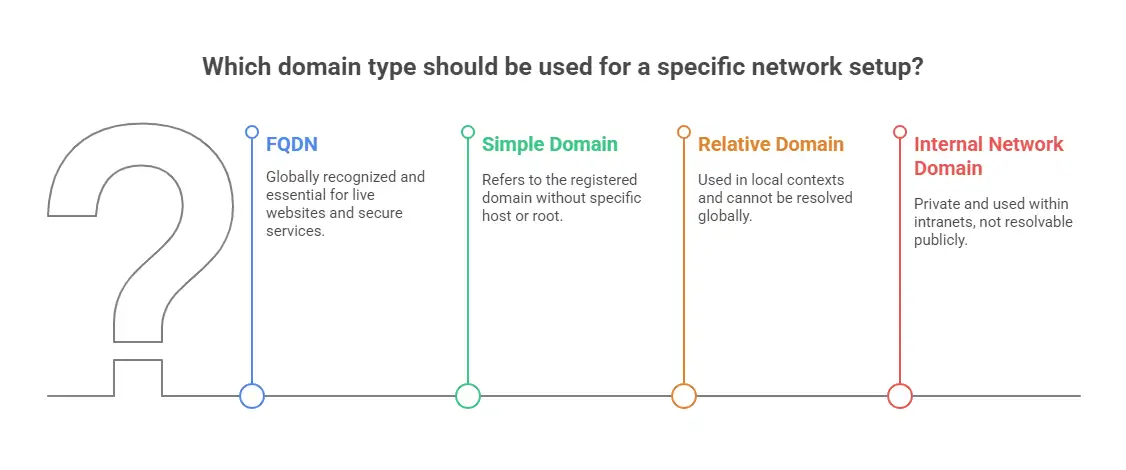
How FQDNs Differ from Other Domain Types
FQDNs are often confused with other types of domain names, especially in local development environments or internal company networks, where the distinction is easy to overlook.
FQDN vs. Simple Domain
A simple domain like example.com refers to the registered domain itself but doesn't include a specific hostname or the trailing dot that indicates the root of the DNS hierarchy. In contrast, www.example.com. is a Fully Qualified Domain Name, explicitly pointing to a specific host and including the root (.) at the end.
FQDN vs. Relative Domain
Relative domains, such as mail or web01.internal, lack the complete structure required to be resolved on the public internet. They're typically used in local contexts and cannot uniquely identify a resource globally.
FQDN vs. Internal Network Domains
Domains like server.local or dev.intra are private and cannot be resolved through public DNS. These are used within intranets or private LAN environments and do not function outside those closed systems.
Only an FQDN is recognized globally by the DNS system and can serve as a reliable, unique identifier for a resource on the Internet. For any live website, email system, or SSL-secured service, using a properly configured FQDN is essential.
How to Design a Smart, Scalable Fully Qualified Domain Name?
Designing a proper FQDN architecture isn't just about picking a catchy name for your site—it's a strategic exercise that impacts SEO, branding, technical scalability, and long-term maintainability. A thoughtful structure can reduce operational costs, improve user experience, and enhance search engine clarity. On the flip side, a messy or inconsistent domain layout can lead to diluted SEO authority, security risks, and management headaches.
Common scenarios to help you structure FQDNs
Scenario 1: Multi-language Websites
Example structure:
-
en.brand.com (English)
-
fr.brand.com (French)
-
zh.brand.com (Chinese)
Why it works:
For global businesses, multilingual websites are essential. Using subdomains for each language improves localization and helps search engines clearly distinguish between regional content.
Benefits:
-
Enhances geo-targeting and multilingual SEO
-
Allows independent deployment per language (different servers or CMS)
-
Supports region-specific performance strategies like local CDNs or caching
Trade-offs:
-
More complex to manage (multiple sites, redirects, translation workflows)
-
Risk of SEO authority being split across subdomains if not well-managed
Scenario 2: Multi-service Platforms
Example structure:
-
app.company.com (main application)
-
support.company.com (customer support)
-
billing.company.com (billing center)
Why it works:
Modern companies often operate multiple digital products or modules. Assigning each system a dedicated subdomain supports security, scalability, and clean DevOps practices.
Benefits:
-
Services can be independently deployed and upgraded
-
Enables stricter security controls per module (e.g., billing with 2FA)
-
Streamlines DevOps: each subdomain can use its own CI/CD pipeline
Trade-offs:
-
Requires thoughtful architecture planning upfront
-
SSL, monitoring, and logging need consistent implementation across subdomains
Scenario 3: Personal Blogs & Marketing Landing Pages
Example structure:
-
blog.johndoe.com (personal blog)
-
promo.brand.com (product launch or campaign)
Why it works:
For content creators or marketers, lightweight pages don't need complex backends. Hosting them on separate subdomains keeps them modular and fast to deploy.
Benefits:
-
Perfect for A/B testing and campaign experimentation
-
Keeps blog updates isolated from the main site
-
Easy to spin up using platforms like Wegic for rapid design-to-launch workflows
Trade-offs:
-
Subdomains need their own SEO strategy—ranking power doesn't fully transfer
-
Inefficient crawl budgets if content updates are frequent but poorly optimized
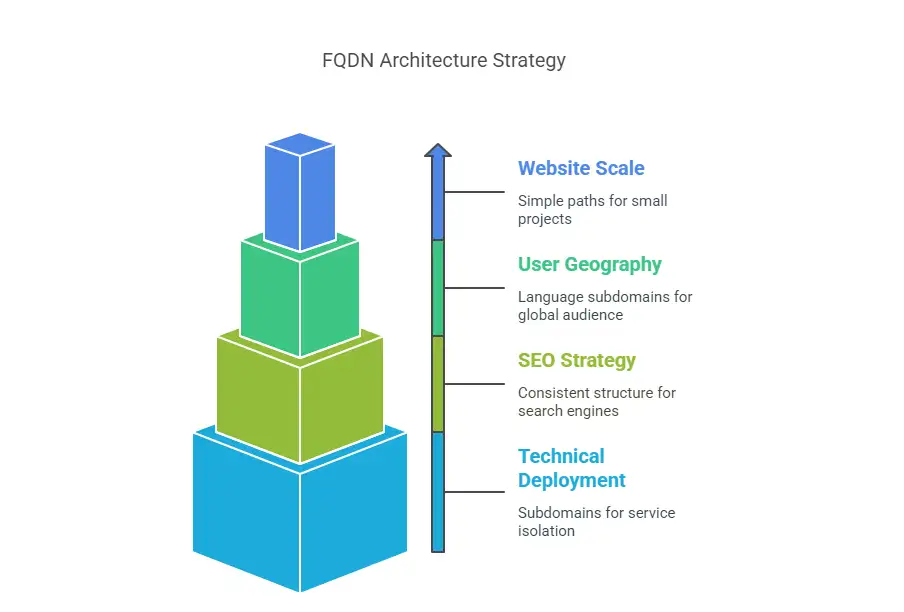
Key Factors to Consider When Designing an FQDN Architecture
Designing a well-structured, fully qualified domain name system goes far beyond picking a URL—it's a strategic decision that directly affects your website's performance, scalability, brand clarity, and SEO success. To build an effective architecture, consider the following dimensions:
1.Website Scale
For small-scale projects or MVPs, using a simple path-based structure (e.g., example.com/blog) may be sufficient. For larger, more complex platforms, modularizing via subdomains (e.g., blog.example.com) enhances clarity and maintainability.
2.User Geography
If you're targeting a global audience, language-based subdomains like en., jp., or fr. help localize experiences and improve search engine relevance in different regions.
3.SEO Strategy
Maintain a clear, consistent structure across your domain hierarchy. Avoid randomly mixing subdomains and subdirectories, as this can confuse search engines and dilute authority.
4.Technical Deployment
If your team uses CI/CD pipelines or maintains microservices, a subdomain-based approach allows for better service isolation and streamlined DevOps workflows.
Wegic Auto-Configures FQDN
With Wegic, building a structured, multilingual website takes just one click. The platform automatically detects your need for language-specific subdomains and generates fully localized site templates—instantly mapping them to addresses like zh.brand.com or en.brand.com without any manual configuration.
Wegic also makes it incredibly easy to manage complex, multi-subdomain architectures. Through a simple chat interface, you can define business modules such as "support," "billing," or "app," and Wegic will automatically create dedicated sub-sites. Each one comes with its own subdomain, routing setup, and built-in security policies, making it ideal for SaaS startups or small IT teams looking to save time and avoid DevOps overhead.
For individual creators and marketers, Wegic also offers a suite of prebuilt templates designed for blogs and landing pages. Just describe your content in a single sentence, and Wegic will generate a fully hosted site like blog.x.com or promo.x.com, complete with responsive design, SEO-friendly structure, and HTTPS enabled by default.
Why Choose Wegic to Configure FQDN and Launch Your Website?
For many beginners, the excitement of buying a domain quickly fades when faced with confusing DNS records, SSL certificate setups, and FQDN configuration. That's where Wegic steps in. Built specifically for digital entrepreneurs, Wegic is an AI-powered website builder that handles everything for you—simply describe your idea in a chat, and within seconds, you'll have a fully functional website that's live, secure, and FQDN-ready.
Click here to build your site
https://wegic.ai/
Wegic automates the entire process from end to end:
-
Smart Domain Suggestions Instantly search and register available domains directly within Wegic, with AI recommending names that suit your brand and audience.
-
One-Click DNS Configuration Skip the technical hassle—no need to manually set A records or CNAMEs. Wegic handles all DNS entries automatically.
-
Automatic SSL Activation HTTPS is enabled by default with no separate certificate application required. Your site is secure from the moment it goes live.
-
Instant FQDN Binding As soon as your site is published, it's bound to a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) that's optimized for SEO (best seo practices), performance, and third-party API integration.
-
Content and Structure Optimization Wegic auto-generates meta tags, clean URLs, favicons, and even robots.txt files—structured to perfectly match your site's FQDN architecture.
Wegic is one of the few platforms on the market that delivers a truly AI-driven experience—from domain registration to live website, complete with FQDN binding and SEO optimization—all without writing a single line of code.
Conclusion
A fully qualified domain name is not just a string of text—it's a complete digital identity, critical for SEO, security, email delivery, and technical integration. Whether you're launching a blog, SaaS product, or multilingual platform, planning your FQDN structure is a strategic decision with lasting impact.
With platforms like Wegic, even non-technical users can confidently create and deploy fully configured, secure, and SEO-friendly qualified domain names—all through a chat-like interface. That's the power of smart automation. Start with the right foundation—domain name structure intelligently, and let your digital presence scale with ease.
Written by
Kimmy
Published on
Jun 5, 2025
Share article
Read more
Our latest blog
Other
Feb 24, 2026
How Freelance Business Analysts Use Data Visualization Portfolios to Justify High Daily Rates
Other
Feb 24, 2026
How Independent Food Scientists Use Compliance Blogs to Attract Emerging Food Brands
Other
Feb 24, 2026
How Freelance Cloud Architects Use Service Packaging to Productize Complex Consulting
Webpages in a minute, powered by Wegic!
With Wegic, transform your needs into stunning, functional websites with advanced AI
Free trial with Wegic, build your site in a click!