Log in
Build Your Site
Find Any Web Page’s Date: Simple Methods
Need to verify when a web page was published or modified? This guide shows how to get the date of any web page using 9 simple, reliable techniques anyone can try.
Any time we surf online, write documents, study newer markets, or deal with online content, we ask ourselves: When was this page created? The date a page is published is not usually easy to find. A few online schedulers just show an “approximately” publishing time. Because information online can change quickly, knowing the age of a page helps you decide if it can be trusted.

This guide shows proven methods to find the publication date of any web page quickly and accurately. Regardless of your role in SEO, content writing, research, or web usage, you'll never be stuck with questions like "how to get the date of any web page?"
What is the Date of Web Pages?
The date shown on a web page indicates important development points for it. This means you can find out the publication date, the date the page was last updated, and the date when search engines first noticed the site. They show us when the published website was last changed and when it was published to the internet. They make it easier to determine whether the data is recent, accurate, and authoritative. People should take special care of this when dealing with news, school tasks, or business information. Having the dates clear allows people to tell if the news is timely and trustworthy.
A web page’s published website date is shown using various formats. For example, the "Published on" notice appears right on the web page. A few types of data are stored in a structured format within the web page’s source code (JSON-LD and Microdata being examples). A few metrics are figured out through details such as HTTP headers, the search engine’s cache, user comments, and what people post on social networks. Yet, it is important to remember that some web pages do not mark the date in the same reliable way. The date of web pages' information can be deliberately falsified or intentionally omitted by some. As a result, having various options for web page time is important for checking sources, following citations, and for employment in SEO, digital forensics, and analyzing content.
Check seo meaning, click the article: ⬇️
How to Get the Date of Any Web Page: 9 Simple Methods
When investigating a web page, looking for information on when it was posted or last changed is necessary. Thanks to this information, research, fact-checking, SEO, and data collection are made easier. However, many web pages are not clear about the date when they were published. You can try various hacks and tricks to help you find the published website date. These nine easy methods will allow you to find the date of any web page. They make it much easier to find out the time for your needs.

Image by Istock
Method 1: HTTP Header Information Analysis Method
The server supplies the
Last-Modified field in the HTTP response header after you analyze the data of a web page. It means the server’s record of the last update to the web page. This way is simple and perfect for static web pages or pages that don’t redirect. It allows you to see if the content is current and if the site remains active. Checking lots of web pages tends to begin with this technique. It results in time and energy saved.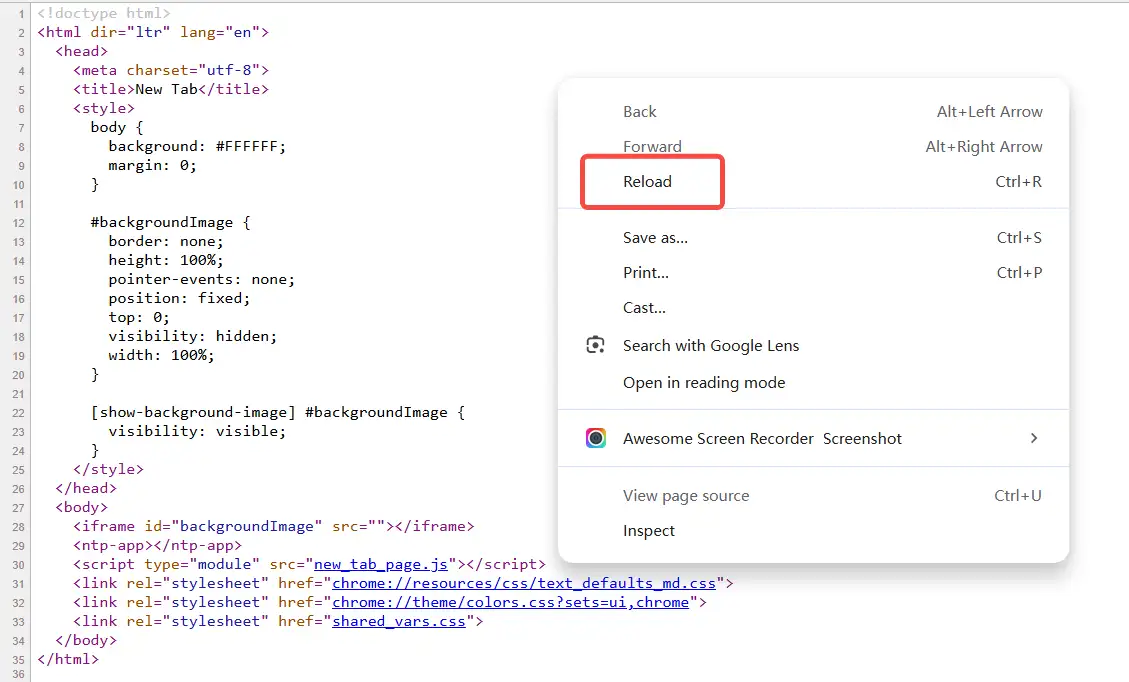
How to get the date of any web page:
-
Use Chrome browser to press F12 to enter the developer tool and switch to the "Network" panel.
-
Refresh the page, click the first HTML request, and check the "
Response Headers" in the "Headers" on the right. -
Find out if there is a
Last-Modifiedfield. -
You can also use curl -I URL to quickly get the response header through the command line.
Notes:
-
Dynamically generated pages (such as PHP, Python backends) often do not have this field.
-
Some field contents are forged by the server.
-
Some CDN acceleration sites may cache old values.
-
This field cannot be relied upon to determine the actual update timing of the content.
-
It needs to be cross-validated in combination with other methods.
Who can use:
-
Developers, SEO experts, and data analysis engineers with a certain technical foundation.
-
Content update monitoring, collection strategy setting, and page version control scenarios with high time sensitivity for web pages.
Method 2: Webpage Metadata Extraction Method
A great number of web pages use HTML meta tags. With these tags, search engines know more about your page. So, when you share your page link on social media, it looks more attractive to readers. You can usually find the publication date and writer’s name stored in the meta tags of an article. Because this information is coded into the site, it is closer to what is actually shown than HTTP headers. Normally, metadata is found in the
<head> part of the web page and can be accessed either by hand or with computer tools. If an article does not give the date it was written, this approach is helpful.
How to get the date of web pages:
-
Use the browser's "View Page Source Code" function to search for keywords such as published_time, article:
published_time,article:published_time,dc.date.issued,dateModified, etc. -
Use crawler tools to batch extract
<meta>tag content. -
Use OpenGraph parsers and Meta tag extraction APIs to achieve automated reading.
Notes:
-
Not all websites follow a unified format.
-
Some sites may not embed time metadata, or have multiple sets of time tags, which can easily cause ambiguity.
-
Be careful about the confusion between page template time and actual content publishing time.
Who can use:
-
Content reviewers, SEO engineers, and data collection practitioners.
-
Monitor the release time of articles on a specific site.
Check metadata meaning, click the article: ⬇️
Method 3: Structured Data Analysis Method
Web pages today often use structured data, which is embedded to make it easier for machines to read, usually as JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa. Search engines use structured data directly, and they can tell the time when an article was first published and the date of its last update. Meta tags are used less often than this method, which is more standardized and run by automated systems.
How to get the date of any web page:
-
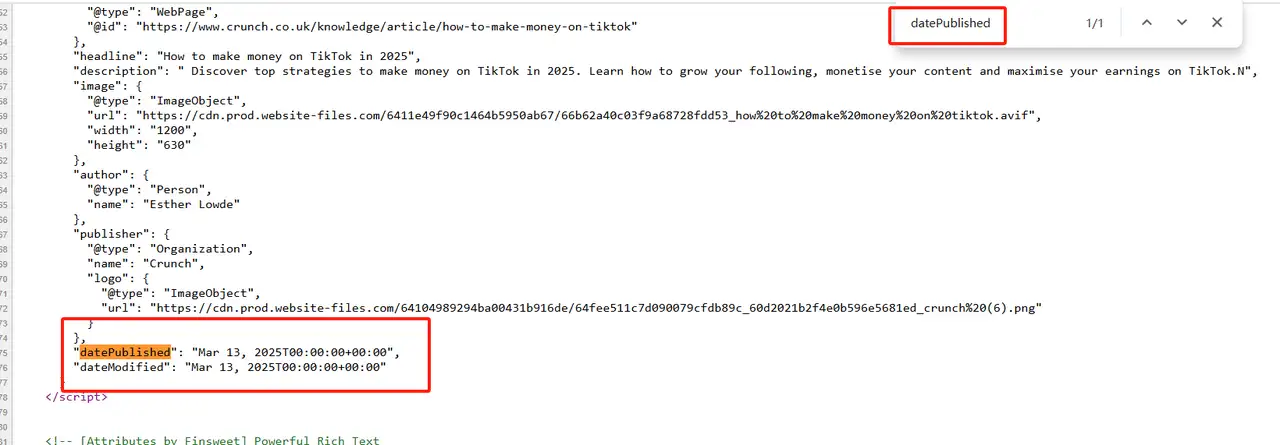
Open the source code of the web page, search for the
application/ld+json tag, and view its embedded content. -
Find the
datePublished,dateModifiedfields. -
You can also use Google's structured data testing tool or Rich Results Tester for visual inspection and extraction.
Notes:
-
Not all websites implement structured data. Its content may be outdated or only filled in formally.
-
Some website templates will copy old fields, resulting in no update of time values.
-
Before using it, you need to confirm whether it conforms to the actual logic.
Who can use:
-
SEO professionals, search engine data analysts, and development engineers.
-
Technical projects that require standardized time data or need to efficiently handle a large number of web page time extraction tasks.
Check seo competitor analysis, click the article: ⬇️
Method 4: Webpage Text Time Identification Method
A lot of websites, for example blogs, news sites, forums, and tutorial pages, include the publish time or author information right within what they post. Because it is for readers, this information is concise and reliable. We can still uncover the times from a webpage if it doesn’t contain metadata.

How to get the date of any web page:
-
The manual method can browse the body of the web page and look for hints such as "
release date", "updated on", "published on", or specific date numbers. -
The automatic method can use crawlers combined with regular rules to extract possible time strings in the page, and further use libraries such as dateparser to standardize the time format.
Notes:
-
There may be multiple time points in the page, such as comment time, user registration time, etc., which are prone to extraction errors.
-
In addition, the format is not uniform, such as "3 days ago" and "May 2024", which need to be localized and adapted.
Who can use:
-
Researchers, content analysts, and automated crawler developers.
-
Especially when it is impossible to obtain information through structured data, this method is of great reference value as a supplementary judgment source.
Method 5: Search Engine Cache Time Method
Google and Bing search engines regularly look at and save web pages for a period. While searching, search engines store copies of web pages together with the time each page was last viewed. This area tells you when the page was first discovered or last modified. Though we can’t see the exact posting time with a cached version, we are able to estimate it roughly. The process is often applied to manage content updating and investigate data origins. You can use it to watch over information and find out where it came from.

How to get the date of any web page:
-
Enter the
cache: web page URLin Google to access the web page cache page and check the cache time displayed in the gray prompt bar at the top. -
Query the first crawl time or update the record of the page through the webmaster platform API or SEO tools.
Notes:
-
Search engine cache is unstable, and some pages may never be cached or have a very low crawling frequency.
-
The cache time may lag for several days or weeks and cannot be used for accurate analysis. It is only suitable for time range estimation.
Who can use:
SEO optimizers, content listing monitors, and search visibility analysts.
Method 6: Wayback Machine Snapshot Comparison Method
Wayback Machine is a digital archiving service offered through the Internet Archive. You can look at a web page as it appeared in the past with historical snapshots. You can discover when the content first went online by looking at these snapshots. It shows you the earliest published website date. Without a date or if a page has been edited or taken down, the date it was online can only be found on the Wayback Machine.
How to get the date of web pages:
-
Access the tool, enter the target web page URL, and view the timeline and snapshot list.
-
Click on different time snapshots to analyze whether they contain the target content or time tags, and find the page that first appeared.
Notes:
-
Not all web pages are archived, and some new web pages or restricted crawling sites will not be included.
-
The snapshot crawling frequency is not high, and there is a time deviation.
-
If the content is updated frequently, it may not be possible to accurately locate the first release version.
Who can use:
-
Legal evidence collectors, media investigators, academic researchers, and digital archaeology enthusiasts.
-
Trace the source of the content or verify the first release time.
Method 7: Website Sitemap Analysis Method
A sitemap file is a file that outlines the organization of a website, letting the search engine know about it. Many times, it will be the last time each page was changed (
Last-modified tag). With this approach, large-scale website structure analysis, page monitoring, and change tracking are made more efficient as the tool can systematically and batch extract the webpage update time. Last-modified can’t always be set to the exact time of new content, but it regularly shows whether a page is current or outdated for sites operating smoothly.
How to get the date of any web page:
-
Try to access sitemate through the root directory of the website, or check the Sitemap address declared in the robots.txt file.
-
After opening, find the
<lastmod>tag under the<url>code, which is the last declared update time of the page. -
Use the sitemap analysis tool to automatically read these fields.
Notes:
-
Not all websites provide sitemaps.
-
Some websites do not necessarily fill in the
last-modifiedfield. -
If the website update time is not synchronized in time, there will be a lag.
Who can use:
-
SEO analysts, content update monitoring tool developers, and data mining teams.
-
Scenarios where you need to track site content changes in batches or create page time indexes.
Method 8: Social Sharing or Comment Time Extraction Method
On many websites that share news, generate blogs, host discussion forums, or act as online stores, user comments and share buttons are often displayed with timestamps. Though these timestamps do not show the date of the page’s publication, they can give us clues about the date it was first posted or shared. This approach is particularly valuable whenever there is no original date available.

How to get the date of any web page:
-
Manually check the comment area or share button floating prompt at the bottom of the webpage, and pay attention to words such as "Published 3 minutes ago" and "Commented on May 23, 2024".
-
Technical users can use crawlers to crawl the time field of the comment module.
-
Analyze whether the data returned by the embedded iframe/JS component contains a timestamp.
Notes:
-
Comments or sharing behaviors do not necessarily occur on the day the content is released.
-
The comment time of some websites is in relative time format (such as "a few hours ago"), which does not have a long-term reference value.
-
Some content may be deleted or the comments may be hidden, resulting in the inability to obtain time information.
Who can use:
-
Media analysts, social communication researchers, and content monitors.
-
Track the time nodes of hot content dissemination, verify the historical activity of articles, or conduct social sentiment analysis.
Method 9: Use Website Date Checkers
Website date check tools help you determine when a web page was built, modified or last seen. They access time information through numerous approaches. Such tools consider the page’s HTTP header, any Meta tags, and any structured data. Some website date checkers will even fetch the time from the page, the same way a browser does while loading. More advanced tools also use saved copies, old records, or search engine data to give extra time details.
How to use website date checkers:
Open websites such as Carbon Dating the Web, SEO Review Tools, PrePost SEO, etc.
Paste the target URL in and click "Check" to get the time analysis results.
Some tools support batch URL input or report generation.
Notes:
-
The accuracy of the tool itself depends on its extraction logic and data source, and the results of different tools may vary slightly.
-
Some websites have set up anti-crawling mechanisms, which cause some tools to return null values.
-
Use several tools for cross-validation.
Who can use:
-
Content planners, editors, academics, researchers, and media reviewers who do not understand code.
-
Quickly determine the time background of a web page or report citations.
Conclusion
Today, when information changes so quickly and comprises many sources, the time a web page is updated matters a lot for its reliability, timeliness, and compliance. Whether you are collecting original site statistics, optimizing the way pages appear, or checking how pages are being delivered, track the time on website pages. Here, we discuss ten easy-to-apply techniques on how to get the date of any web page, ranging from examining HTTP logs to using structured data, cache features, and website date checkers. Both basic and advanced approaches are used to support people in solving problems at different skill levels.
Naturally, getting access to the web page is the first step to learning the web page’s logic. Improving content management and publishing largely depends on using a website builder that is flexible, user-maintained, and doesn’t require coding. Here we suggest you try Wegic, an intelligent website-building platform for those who do not code. Wegic powers easy and natural chats, and its users can shape the website’s layout and produce content by talking to the platform. The AI in Wegic automatically designs solutions that stick to a brand’s look and industry, leaving you with less work. Whether a blogger, brand, designer, or freelance entrepreneur, Wegic helps you build websites that match your needs.
Written by
Kimmy
Published on
Jun 5, 2025
Share article
Read more
Our latest blog
Tool
Feb 27, 2026
How Interior Designers Use Interactive Portfolio Galleries to Attract High-End Clients
Marketing
Feb 27, 2026
How Freelance Dance Instructors Use Online Booking Pages to Fill Classes Automatically
Tool
Feb 26, 2026
How Independent Nurse Practitioners Use Trust-Building Profiles to Launch Private Practices
Webpages in a minute, powered by Wegic!
With Wegic, transform your needs into stunning, functional websites with advanced AI
Free trial with Wegic, build your site in a click!