Log in
Build Your Site
PNG vs JPG: Choose the Right File Format for Your Site
Learn the differences between PNG and JPG formats and how to optimize them for web performance. Discover which format suits your needs for transparency, image quality, and loading speed.

PNG and JPG are two different formats of images. Each of these formats has its respective advantages and limitations. In this blog, I will compare the differences between PNG and JPG, their strengths, and when to use each. In addition, we’ll also discuss optimization techniques to improve your site's performance and SEO. By reading this blog, our audience can have a better understanding of these two image formats and choose the right format for your design.
PNG vs JPG: What is the Definition?
What is PNG?
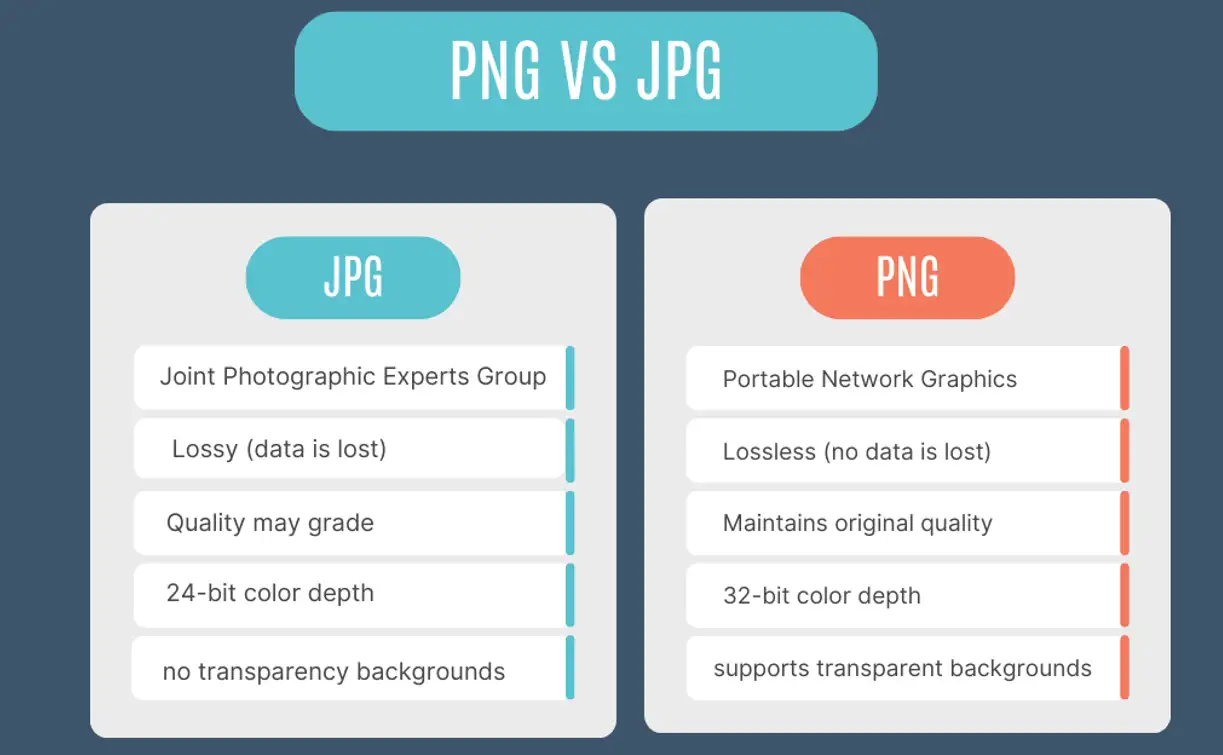
PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics.
The history of PNG can be traced back to 1995. At that time, GIF was one of the most common formats on the Internet, but due to patent and technical restrictions, developers and image experts began to develop a new image format, namely PNG, which was officially released in 1996.
PNG format images have many advantages. PNG improves the quality of images through lossless compression technology, supports more colors and transparency functions, and better preserves the details of images. Today, PNG has become a widely used image format on the Internet.
What is JPG?
JPG (JPEG) stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group.
Its history can be traced back as early as 1986. In the 1980s, with the development of digital image technology, storing high-quality images required a lot of disk space, and transmitting these images took up a lot of bandwidth. So people urgently needed a technology that could compress image size while retaining image quality as much as possible, JPEG came into being. In 1992, the JPEG standard was officially released.
By the way, JPG and JPEG are the same thing! The only reason for the difference is that early versions of Windows had a limitation where file extensions could only be three characters long, so JPEG was shortened to JPG.
JPG is a lossy compression algorithm that discards details that are not easy to find in the picture to meet the needs of compressing pictures. For example, some natural scenery and portraits are very suitable for using the JPEG format because these images are complex in color and rich in detail.
Because JPG can significantly compress file size while maintaining high image quality, it has now become one of the most widely used image file formats in the world, especially in some occasions that require efficient storage and transmission of photos, such as the Internet, social media, and mobile devices.
PNG vs JPG: What are the Key Differences?
After introducing the development history of PNG and JPG, I will further compare the two image formats, including their compression methods, transparent backgrounds, file size, image quality, color depth, and so on.
PNG vs JPG: Compression
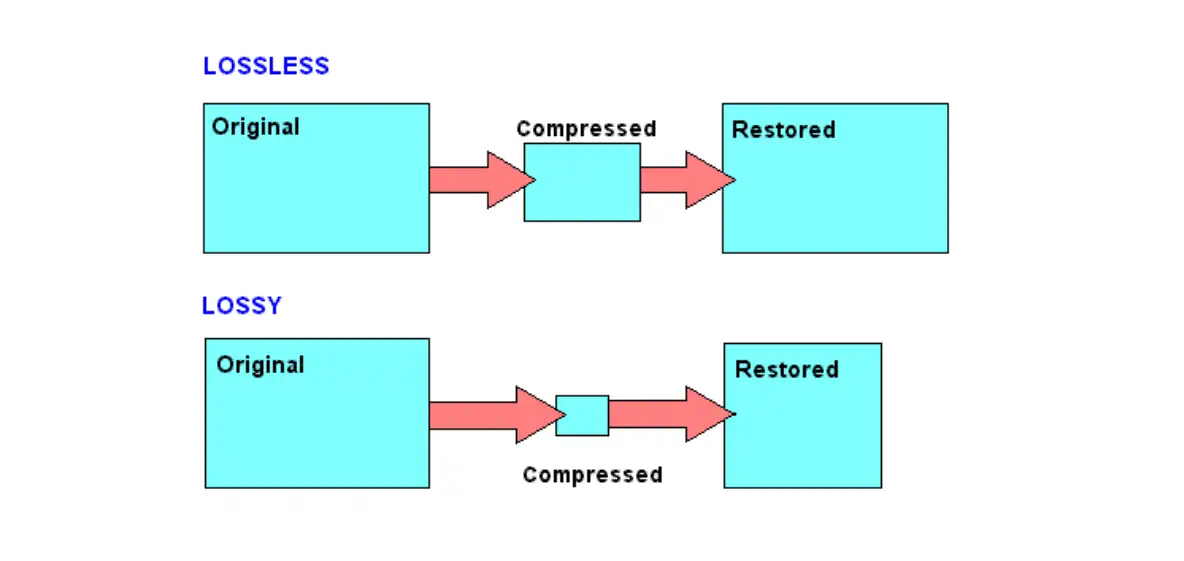
PNG uses lossless compression technology. It means that when you use PNG to compress your image, no data is lost. It can well maintain the quality of your image. Therefore, PNG format is particularly suitable for images that need to maintain quality, such as logos, graphics with text, and images with sharp edges.
However, although the image still maintains high quality, the image file will be larger than that of lossy algorithms.
JPG uses a lossy compression algorithm. That means that when you compress the image, some inconspicuous data may be discarded to significantly reduce your file size.
Although JPG can greatly compress the file size, it will also damage the quality of the image. However, this is controllable, and you can control how much data to discard according to your needs. You can maintain high quality as much as possible while effectively reducing the file size. This makes JPG ideal for photographs and images with many colors or gradients because the slight loss of detail might not be noticeable to the viewer.
PNG vs JPG: Transparency Support
PNG supports transparency, but JPG does not.
Some readers may not have studied design and are not sure what transparency means. Before making a comparison, let me briefly explain the meaning of transparency.
Transparency simply means that some parts of the image are "invisible", or transparent. Suppose you have a company logo. If the background of this logo is white, then when you put it on a website with a blue background, you will see white squares surrounding your logo, which does not look very beautiful. But if the background of this logo is transparent when you put it on any color background, only the logo will be seen, and the background part will not be displayed, which looks more professional and clean.
PNG supports transparency. For example, when you save a logo image in PNG format, the background can be transparent, so no matter what color background you put this photo on, your audience will only see your logo. That’s why so many icons, logos, or images with complex shapes prefer PNG.
JPG, on the other hand, doesn’t support transparency. It doesn’t have this feature. Its background is always a solid color, such as white or other colors. If you save a logo as a JPG, even if you want the background to be transparent, it will become white or another default color. This will cause the background color to not match the web page color or other elements when you use this image, and it will not meet your expectations.

PNG vs JPG: Size
PNG file sizes are generally larger, and JPG files are smaller.
As mentioned at the beginning, since PNG uses lossless compression technology, no data is lost during compression, so the file is naturally larger. And, with some additional features such as support for transparency, it is quite normal for those larger PNG files.
On the contrary, JPG uses a lossy algorithm, which discards some insignificant data during the compression, so the file is correspondingly smaller. JPG files are smaller, so they are very suitable for websites because they can reduce the speed of file loading. Also, websites do not have such urgent needs for high-quality images.
PNG vs JPG: Image Quality
PNG performs better in maintaining image quality than JPG.
PNG images can maintain very high image quality even after editing or saving multiple times. So people often choose PNG format when they make images with text, sharp lines, or detailed graphics. If you have requirements for the clarity and accuracy of the image, PNG format is obviously your best choice because it will not lose data during compression.
The image quality of the JPG format cannot be maintained as good as PNG ones, especially when you save it many times, you will find obvious degradation in image quality due to its lossy compression. If you have requirements for the file size and you don’t need perfect clarity at the same time, you can consider using JPG format.

PNG vs JPG: Color Depth
PNG has a 32-bit color depth while JPG has a 24-bit color depth.
Some of you might not know what color depth is. Here I would like to give a simple explanation of this concept. Color depth is related to the transparency we just talked about. Let me first introduce the concept of color depth. Simply put, color depth refers to the number of colors that can be displayed for each pixel in an image. The more colors, the richer the details and color performance of the image.
We know the JPG format has 24-bit color depth. 24-bit color depth images can display about 16 million colors. That's a lot of colors, so it's good for displaying photos, gradients, or other images with rich colors. Generally speaking, most of the images we see in daily life, such as the ones we see on the Internet, are 24-bit color depth.
The PNG format has 32-bit color depth. 32-bit color-depth is similar to 24-bit color-depth. The number of colors in 32-bit color depth is the same as 24-bit color depth, both are 16 million colors, but 32-bit color depth has a special feature over 24-bit color depth: support for transparency. This means that in addition to being able to display 16 million colors, the image can also make part of the image "invisible" (transparent).
This is useful for design, such as when you have a company logo and you want the background to be transparent so that the logo can be placed on any background without white or other color boxes around it.
In a word, 24-bit JPG has no transparency, but its high color depth makes it great for photos. 32-bit PNG has high color depth and transparency, making it perfect for logos or images with clear backgrounds.
PNG vs JPG: When to Use PNG or JPG?
Knowing the differences between PNG and JPG, you may have a better understanding of their respective strengths and limitations. I know some of you might still have questions when making decisions. So, in this part, I will talk about when to use PNG or JPG to help you choose the right one for your design.
PNG
Now, let's start with PNG. PNG will be your go-to format in the following situations.
01.Images with Transparency (logos, icons)
If you need transparency, PNG is your primary choice, especially when you are working on web elements such as icons, logos, or buttons because these elements have high requirements for transparency and clarity.
02.Graphics with Sharp Edges or text (charts, banners)
If your design contains sharp edges or text, it will be more suitable to choose PNG format because PNG excels at preserving sharp details, like the edges of text or graphics with clean lines.
03.High-quality Images with Fine Details (screenshots)
If your images have great details, and those details must be reserved, PNG is the go-to format. For images like screenshots or your product images where every pixel matters, PNG is an ideal choice because PNG uses lossless compression. It can retain all its original data and preserve every detail, so you can demonstrate your design to the audience more completely.
PNG has so many advantages, especially its transparency support and high resolution. However, its file size is still a big limitation in many design cases.
JPG
In the following situations, JPG will be a more ideal choice for you.
01.Photos with Complex Colors and Gradients
For the images, especially the photographs of landscapes or portraits with rich color layers, JPG is an ideal choice. JPG is excellent at compressing images with smooth gradients or many color variations
02.File Size and Speed are More Important than Transparency
If the image does not need a transparent background, or compared to transparency, file size, and loading speed are more important, then JPG is an ideal choice.
For example, if you are working on your blogs or e-commerce site, the loading speed is much more important than transparency because it will directly influence user experience and SEO. Or if you want to share your photos on social media platforms, JPG is enough to meet your needs as transparency is not usually needed.
In these cases, file size and speed take precedence over the need for transparency, so using JPG will be better.
How to Optimize Your Images for Web Performance
File size impacts website performance and SEO ranking indirectly. If your file size is too large, it will affect the page loading speed, thus creating a negative effect on user experience and SEO rankings. So, it is important to learn how to compress and optimize images to improve website performance and rankings. Here are some effective ways:
-
Compress the Image
-
Resize Images
-
Adjust Quality Settings (JPG)
-
Reduce Color Depth (PNG)
-
Use Lazy Loading
01.Compress the Image
First, you can use tools to compress images directly, such as TinyPNG, TinyJPG, or ImageOptim. These tools help reduce file size, thus improving page loading times.
02.Resize Images
Resizing images also plays an important role in improving performance. You should only use the dimensions your website needs. Image dimensions refer to the width and height of an image, typically measured in pixels (e.g., 800x600). If a webpage only needs an image to be 400 pixels wide, but your image is 2000 pixels wide, you should resize it to match the 400 pixels. This reduces both the dimension and file size, making it load faster.
03.Adjust Quality Settings (JPG)
In addition, you can adjust your quality setting. When saving JPG images, there’s an option to control the quality level. If you use higher compression, your image quality will be lower, and your file size will be smaller. You can set the quality between 75-85% because it can create a balance between good image appearance and a smaller file size.
04.Reduce Color Depth (PNG)
We have discussed color depth above. In fact, PNG images can support different color depths, including 24-bit and 32-bit. The 32-bit is the highest and it includes transparency. The 24-bit has no transparency but still maintains full-color quality. That means if your PNG image doesn’t require transparency, you can reduce its color depth to 24-bit. This will significantly minimize file size and increase loading speed while preserving image quality.
05.Use Lazy Loading
Lazy loading is another effective way for both JPG and PNG. When you apply lazy loading, the images only load when they appear on the user’s screen, reducing the initial page load time.

What about Other Image Formats?
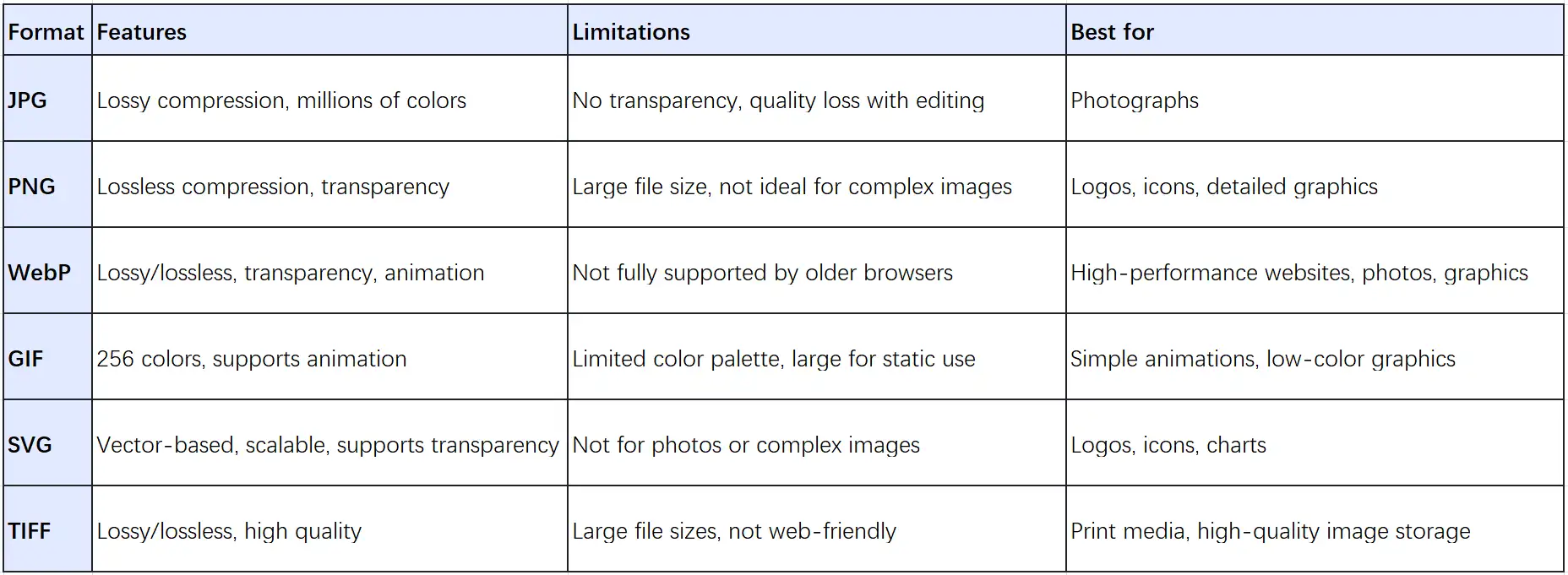
Aside from PNG and JPEG, there are various other image formats such as WebP, GIF, SVG, and TIFF.
WebP: A modern image format by Google. It offers both lossy and lossless compression, along with transparency and animation support.
GIF: A format known for supporting simple animations and transparent backgrounds. However, it is limited to 256 colors.
SVG: A vector-based format that can scale to any size without losing quality, perfect for logos and icons.
TIFF: A high-quality format used for printing or professional photography. It supports both lossy and lossless compression. It creates large files, making them unsuitable for the web.
Below is a table comparing the features and limitations of each format for your reference.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have explained what PNG and JPG are, and we also compare their features and drawbacks. I guess you already have a deeper understanding of PNG and JPG formats.
When it comes to choosing between PNG and JPG, there’s no "one size fits all." Neither format is inherently better—it all depends on what you need for your design. PNG is great for images that need transparency or crisp details, while JPG is perfect for photos and when file size is a top priority. Think about what’s most important to you—image quality, speed, or flexibility—and pick the format that fits your needs.
FAQ
Can I convert a JPG to PNG without losing quality?
Yes, you can convert a JPG to PNG, but the image will not regain any quality lost in the original JPG compression. The PNG will preserve the current quality level and offer transparency if needed.
Are there other image formats I should consider for web use?
Yes, modern formats like WebP offer both small file sizes and good quality, making them excellent for web performance. However, browser support may vary, so it's important to ensure compatibility with your audience's devices.
Can I use both PNG and JPG on the same website?
Yes, you can use both formats. For example, use PNG for logos or icons with transparency and JPG for large photos where file size and speed matter more.
Written by
Kimmy
Published on
Nov 10, 2024
Share article
Read more
Our latest blog
Webpages in a minute, powered by Wegic!
With Wegic, transform your needs into stunning, functional websites with advanced AI
Free trial with Wegic, build your site in a click!