Log in
Build Your Site
How to Choose the Best Video Format for Your Website
In this blog post, you will learn about the 6 video formats and know how to choose the best video format for your website.
Better than words and pictures, videos are particularly powerful in making people remember things. Video can introduce many of your ideas to visitors in just ten seconds or so with the help of visual and auditory elements, enabling information sharing. You can use videos on your website to help you grab the attention of your visitors, make your customers like you, and create an emotional connection with them.
If you also want to make your website dynamic by inserting videos, you will find that there are many video formats. How can you choose the best video format for your website?
In this article, we will cover what video formats are, different kinds of video formats with their features, and factors to take into account when choosing video formats. Finally, you will know how to choose the best video format for your website and how to insert the video into your website! Let's get started!

Step1: Choose the Best Video Format — Understand What It Is

Video format refers to how video information is stored on a digital device or server. We can identify the video formats by using file extensions such as ".mp4". It affects how the video data is compressed and decompressed so that it can be played on a variety of media players and devices. It affects file size and download or streaming speed.
Different formats are better suited for specific types of playback or devices. Choosing the best video format helps maintain video quality and ensure compatibility with playback devices. For example, MOV can be used by iPhone users for quick social media uploads, but you can choose AVI format videos for more convenient use on Windows.
The Two Components of a Video File
Video files have two main parts: format (also called container) and codec. Formats and codecs aren’t the same thing—they each serve a different purpose. Don’t worry if these words seem confusing. We’ll explain the differences in a simple way to help you understand how video files work.
1.Codec
Codecs compress and encode content, reducing the storage space required to hold each file. This compressed video is saved as a single file.
Codecs combine similar data, reduce the number of colors, and lower the resolution to make files smaller.
There are two types of compression methods: "lossy" and "lossless." Lossy compression removes or combines parts of the file, making it smaller but lowering quality with each edit. Lossless compression keeps all the original data, so the file stays high-quality but is larger in size.
2.Format
Now that we've explained video codecs, one of the two components of a video format, you might still be wondering what a video container is.
The Format(Container) stores data, such as audio, video, and captions. As you might imagine a container, a video container is used to keep all the elements of a file together so that they can be played in sync.
All video containers can hold data related to audio and video, but they may differ in their ability to hold elements beyond these. Some video containers can hold metadata and captions, while others can only hold audio and video elements.
As mentioned above, video containers can be identified by their file extensions, including .mp4, .mov, and .avi.
3.The Difference Between Codec and Video Format/Container
In general, the codec is about the software and the things that happen within the file, and the format(container) is the thing that contains it all (including the codecs). The format names classify each file type. When you look at a video file type, like MOV, you see the name of the format.
Step 2: Choose the Best Video Format — Types to Explore
Choosing the best video format for your website requires understanding different types of video formats and their characteristics. Here are the six most common video formats
1. MP4
MP4 is the most common and popular video format. MP4 has the widest compatibility and can be played on most other devices. It is capable of storing audio, video, subtitles, text, and static images. MP4 uses the MPEG-4 encoding algorithm to store video and audio files as well as text, but the clarity is lower than in some other formats. MP4 is ideal for videos posted on YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Pros
-
Wide Compatibility: Supported by most digital devices and media players.
-
Efficient Compression: Delivers high-quality videos with smaller file sizes.
-
Optimized for Streaming: Well-suited for online video streaming.
-
Platform Acceptance: Accepted by most video-sharing platforms.
Cons
-
Prone to Corruption: Files in this format may be more susceptible to corruption.
-
Potential Quality Loss: Video clarity and color depth may decrease slightly after processing, which could lead to a corrupted MP4 file error message.
-
Piracy Concerns: Its popularity and ease of use make it a common target for piracy.
2.WEBM
WEBM is a free video format created by Google for HTML5. Because it’s open source, people can review or edit it. WEBM works with HTML and plays right in the browser, so you don’t need extra Flash Player or other plug-ins. The files are small, which makes them load quickly and stream easily. They also don’t need much computing power to process, which makes WEBM a great choice for videos you watch in the browser.
Pros:
-
Fast loading time: WEBM videos load quickly and can play directly in the browser.
-
High-quality playback: The format provides good video quality in a small file size.
-
Browser-friendly: Major browsers like Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Opera support WEBM.
-
Easy to add to websites: It’s simple to embed in a website, which can improve design and content.
Cons:
-
Limited mobile compatibility: Not all mobile devices can play WEBM videos directly in HTML.
3.MOV
Apple created the MOV file format. It is high-quality and, like MP4s, can hold audio, video, subtitles, and more in one file. Apple designed this format for QuickTime Player, making it the best choice for Apple devices. Windows users can also play MOV files by downloading QuickTime Player, but the format is generally better for Apple users to watch or edit.
Pros:
-
High Definition with Compact Size: Offers high-definition video quality while maintaining a relatively small file size.
-
Editing-Friendly: Supports splitting, making it ideal for video editors.
-
Subtitles Support: Can store subtitles alongside video and audio.
Cons:
-
Limited Compatibility: Often requires QuickTime Player for playback.
-
Potential Data Loss: Compression may result in data loss.
-
Apple Dependency: Playback and functionality are heavily reliant on Apple support.
4.AVI
As Microsoft's response to MOV, AVI was developed in 1995, and it is one of the oldest video file formats. It is best suited for users who need to upload videos to multiple platforms or those who use them across different browsers or Windows because AVI videos are accepted almost everywhere. However, they are not very suitable for streaming and sharing for large file sizes.
Pros:
High Video Quality: It delivers excellent audio and video quality, making it ideal for DVD recording.
Strong Compatibility: It works seamlessly across major operating systems (macOS, Windows, Linux) and web browsers.
Cons:
Large File Size: It requires significant storage space on your device.
Not Ideal for Streaming or Sharing: Streaming may be delayed due to the large file size.
Compression Quality Loss: Some quality degradation occurs during compression.
Lack of Subtitle Data: It does not support subtitle data, limiting accessibility options.
5.WMV
WMV (Windows Media Video) is a video file format developed by Microsoft. It is designed to improve online visibility and is the successor to AVI. WMV files are supported on both Windows devices and Apple devices with Windows Media Player installed.
Pros:
HD Video Support: WMV works with 1080p HD videos, perfect for high-quality playback.
Small File Size: WMV keeps good quality while being smaller in size. This makes it easy to share by email or upload to cloud services like Google Drive.
Best for Windows Users: It’s the go-to format for Windows users and works well with Windows Movie Maker.
Built-in Licensing: WMV has copyright and licensing features, making it great for distributing or selling digital videos.
Cons:
Compatibility Issues: WMV mostly works on Windows PCs and some specific players, so it’s limited to Mac or mobile devices.
Quality Loss: Compressing the video can reduce quality, and you can’t adjust the compression, which may lead to poor video quality.
Fragile Files: WMV files can get damaged, causing issues like lag or preventing the video from playing.
6.MKV
The MKV video format was created in Russia. It supports many different codecs at once. Like WEBM, MKV video is open-source, so people can easily process it. In addition, it contains various types of content in one file, such as audio, video, subtitles, metadata, and menus.
Pros:
High Quality: MKV can maintain great video quality without losing data when compressed.
Multi-Codec Support: It allows you to store both audio and video in one file.
Flexibility: It supports chapters, subtitles, and menus.
Great for Big Screens: This kind of video works well on players of big-screen devices, such as TVs and computers.
Cons:
Large File Size: MKV files are bigger than other formats, so they need more storage.
Complex Compression: The compression process is harder, which can cause compatibility problems with some devices.
Not Compatible with Apple Devices: MKV doesn’t work well on many Apple devices.
Audio Problems: MKV sometimes has audio sync issues, which will affect the viewing experience compared to formats like MP4.
Step3: Choose the Best Video Format — Factors to Consider
Choosing the best video file format is crucial for optimizing site performance. If you don't choose the right format, the video can't be uploaded successfully to the target platform. Here are five factors you can take into consideration when picking the right video format:
1.Video Quality
Video quality depends on resolution, color depth, and overall appearance. Different formats offer different quality levels.
High-quality videos can look amazing, but they can be hard to download, share, or convert. Formats like MOV and AVI offer excellent quality but often have large file sizes, making them slow to upload, which can delay your work.
When choosing a video format, consider how much time you have to compress and the quality you want to show. Pick a format that fits your needs. If viewers save the video, use a format with less compression, like AVI, to keep the quality high. Balancing quality, file size, and compatibility is key to sharing videos easily.
2.Compression
If you have limited bandwidth or storage, check compatibility requirements like file size before choosing a video format. If the video file is too large, use a compression tool to reduce it. Compression efficiency affects both file size and quality.
Formats like MP4 and WEBM offer good compression. They reduce file size without a big drop in quality, which is useful for streaming or storing lots of videos.
Like some audio formats, most video formats lose data during compression. The format you choose should balance quality with ease of use. A good balance between compression and quality helps save resources and keeps the viewing experience enjoyable.
3.Video Compatibility
Compatibility means whether a video can play on your audience’s device or media player.
To pick the right format, think about your audience and their devices. Different platforms and browsers only support certain video formats. For example, TikTok only lets you upload MOV and MP4 files, so you can’t upload a WEBM file there. Make sure your video works with the platform you’re using.
If your audience will watch your video on the web, choose a video format that works with most browsers. WEBM and MP4 work on nearly all browsers, while other formats might only work on specific ones. Using these web-friendly formats means visitors won’t need to download extra media players to watch your videos.
4.Visitors' Computer Operating System
Find out which version of the computer operating system your visitors have. Some video formats only work with certain versions. If they have a newer version, they can open more types of video files. If they have an older version, choose a video format that works with those older models. For example, WMV files are good for older Windows computers.
5.Video Processing Tools
Finally, know which video file types your tools can create and edit. For example, Apple products don’t support WMV files. So, if you’re creating videos on an iPhone, avoid using this file type.
Step4: Choose the Best Video Format for Your Website
After knowing the above information, it is time to choose the best video format for your website. In summary, we recommend WEBM videos. They load quickly and work well on websites. MP4 and AVI videos are also good choices. They work with many devices and browsers.
Step 5: Use Wegic to Embed Videos on Your Website Easily
Click on the picture below right away and start your website-building journey!
Wegic is a no-code online website-building tool that supports website creation and management through natural conversational interaction. Simply describe your needs or ideas, and Wegic will guide you step by step to create a professional website based on the key points.
Wegic not only supports you to embed a Youtube video but also supports you to upload a video from your computer to your website. When you use Wegic to build a website, you only need to follow the instructions in the picture below to insert the computer video into the website quickly:
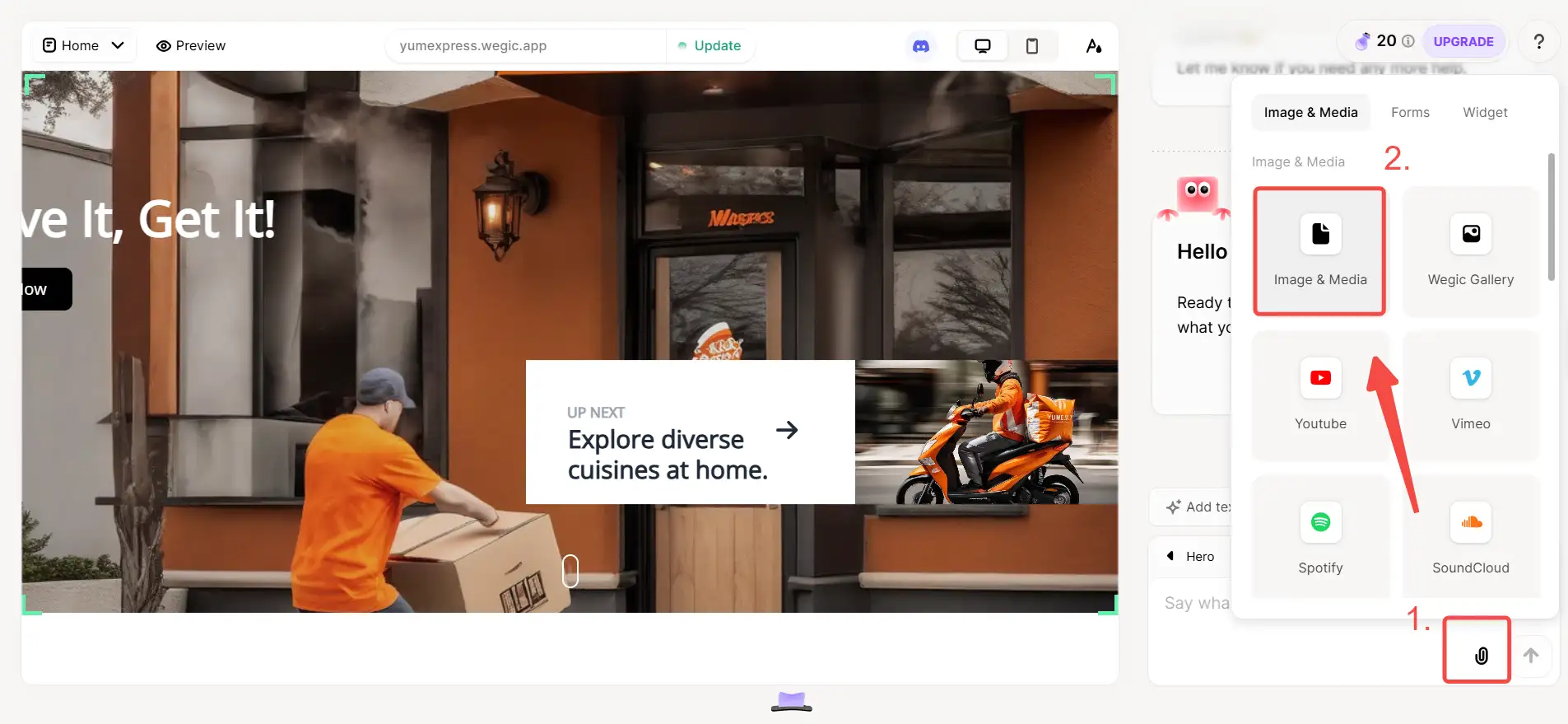
After you click the Upload icon, you can see the video files on your computer. At this time, you only need to select the right video format file.

Explore more about Wegic in the Help Center.
Final Thoughts
Inserting videos into web pages is a good choice, both in terms of optimizing user experience and enhancing brand image. To help you choose the best video format, you need to understand the characteristics of different video formats and their impact on web page performance.
We recommend that you choose video formats, including WebM, MP4, and AVI. When you have chosen the best video format for a website, remember to use Wegic to build it and embed videos into it!
Written by
Kimmy
Published on
Dec 4, 2024
Share article
Read more
Our latest blog
Tool
Feb 27, 2026
How Interior Designers Use Interactive Portfolio Galleries to Attract High-End Clients
Marketing
Feb 27, 2026
How Freelance Dance Instructors Use Online Booking Pages to Fill Classes Automatically
Tool
Feb 26, 2026
How Independent Nurse Practitioners Use Trust-Building Profiles to Launch Private Practices
Webpages in a minute, powered by Wegic!
With Wegic, transform your needs into stunning, functional websites with advanced AI
Free trial with Wegic, build your site in a click!
