Log in
Build Your Site
Beta Test vs Alpha Test: What’s the Difference?
Unlock the secrets of software testing! Explore the vital differences between alpha test vs beta test and their roles in a successful software release.
Within the software development field, the process of releasing any software is done orderly to prevent major usability problems from the consumers before the official release. Normally associated with assurance, testing into these different periods is what is known as a beta test and an alpha test. The differences between the two lie in their aim, the participants, and the phase at which they are conducted. It is not possible to mention the two test phases without indicating how they are applied with regard to success, since beta test vs alpha test is significant in the software development process.

Why People Need Alpha Test and Beta Test: What They Offer
Beta and alpha are both acceptance testing; acceptance testing is that sweaty-and-technical phase through which it is decided whether a software system has fulfilled the specified requirements and is ready to become a living organism. The testing intends to identify defects, pick out usability problems, and receive feedback that can provide inputs toward improvements felt necessary before the product is ever exposed to a larger audience.
Typically, an alpha test is a kind of formal testing and is the earliest phase of development undertaken by the developers of the software themselves. The plan is to identify every possible defect and anomaly at this stage of the development. Alpha testing is one of the several ways engineers make sure that the vital functionalities operate and the application is functional enough before letting anybody else use it. This tends to lessen the number of serious problems that may occur in the future, which, in turn, saves time and other resources. During such alpha testing, different components of the application may be inspected and verified by, for example, doing system testing–an act developers as much as possible employ. The importance of these lessons learnt during alpha testing is such that it allows incorporating changes into the design in a very short time.
On the other hand, a beta test takes testing to another level, outside of the internal team, and this incorporates actual users in maximally real conditions. This stage is fundamental in gauging the performance of the software when put to various stresses, as well as gauging the responses of a wider audience to the software. A beta test gives an insight into the usability, effectiveness, and interworking of the system, which may be more difficult, if not impossible, to test in a confined setting. It assists in confirming the suitability of the product within the intended market and appreciates potential hindrances that become apparent only when individuals of diverging competencies and paradigms make consistent use of the product. This is the point where the merit of user testing is greatly appreciated, as it is able to record raw user interaction, which helps in avoiding product recalls. Before release, during a beta stage, companies are able to determine the level of satisfaction of the customers and make possible user-oriented reading adjustments before the product is finally launched.
Therefore, both are part of comprehensive testing considerations. When complete, useful feedback is to be obtained; usually, both alpha and beta testing are practiced. The tests greatly reduce the possibility of any applications of a product going untested, as feedback is gathered internally and externally. Thus, only high-quality software can finally be released.
Key Differences Between Beta Test and Alpha Test
Despite the fact that alpha testing and beta testing are of no less importance when it comes to the quality of software, they are performed by different individuals, in different ways, and for different purposes. The most basic difference between beta test vs alpha test is about the people who are involved in testing, the place of testing, and the focus of testing.
Testing Environment and Participants:
- Alpha Test: An initial testing process, otherwise known as an Alpha test, is mostly conducted within an organization and always in the development or quality assurance environment. It is therefore the norm for members of the organization who are mostly developers and quality assurance engineers or any staff member who directly forms part of the project team, to conduct the testing exercise as internal testers. The internal testers have extensive insight into the structure and design of the system; hence, they can identify considerably severe technical problems. This type of checking is pretty much directed practice, given that internal testers are involved, and so the circle of response is usually quite short and streamlined. The emphasis on alpha tests is not only towards error tracking but also functionality, and utilizes the concept of combining the black box testing with the white box testing strategy.
- Beta Test: Beta testing, in contrast, is an external test in the real-world-environment of the user. It considers external testers who are true end users of the software. These external testers provide invaluable insights in how the software holds up under myriad real-life situations that are often impossible to simulate internally. The beta testers have various backgrounds, mimicking the wider audience for the product, that is, the target customers of the product, providing different opinions on the easy-to-use features, efficiency, and total effect of the user base, among other such ideas. Black boxing testing is predominant at this stage, as all the external testers see nothing of the code or the design.
- Alpha Test: An alpha test phase is a preliminary test that occurs much earlier in the development process before the software is considered feature complete or enters the later refinement stages. It dealt with the simple fundamental question of "will this thing work as expected?" The alpha test cycle is longer for each build, and these cycles help the programmers to debug and test again once the errors have been remedied. It precedes the beta test to allow stable operation of the product before introducing it to a wider audience.
- Beta Test: A beta test is the final step in testing before putting software on the market. It answers the question: "Is the product favored by clients?" This phase usually lasts a few weeks, depending on late feedback and validation. The idea is to ensure that the product is ready for the user and tackle any critical issues that may prevent the successful application from being launched. The feedback gathered during the beta test from these external testers will be directly reflected in the finishing of the software and its readiness for release.
Scope and Focus:
- Alpha Test: The key purpose of alpha testing is to assess the usability and functionality of an application. The goal is to discover all possible errors and bugs in the product. At this stage, developers are busy with bug fixing and strive to correct detected defects to make the kernel stable. This is dose to a large extent, as in alpha, there is often some thorough system testing which isolates the use of certain individual components of the system.
- Beta Test:. The product is. While a beta test truly covers the working of the product in detail, it is not limited to bug-related tasks, as they are also collected during the process. A beta test is mainly conducted to identify the overall effectiveness of the product, such as how easy or difficult it is to use, how fast or slow, how secure or insecure the product is, and how reliable the product is in the environment. Feedback on User Experience in every task is also key as it curtails the number of defects incurred by the product. This is an aspect where user testing plays a significant role because it deals with how the users in perspective were able to use the product.
To conclude, the difference between beta test vs alpha test is distinct: alpha test includes an early stage, comprehensive, and underground assessment of the features and bugs by internal testers. On the other hand, beta testing refers to an intermediate stage and superficial examination carried out by outside testers, confirming if the market is ready and the users have accepted the product, which finally leads to the effective launch of the software.
Key Similarities Between Beta Test and Alpha Test
Although they starkly vary in practice, they share various fundamental aspects that warrant their importance in the software development life cycle. Both of these are equally critical for a timely release of high-quality software and a positive user experience.
- Goal of Quality Assurance: Beta and alpha tests are primarily conducted to ensure that the product being tested is of high quality. The processes aim at ensuring completeness before releasing it to the wider audience or markets. Both these processes focus on improving the quality of the product in terms of stability, reliability, and usability.

- Feedback Mechanism: Both stages are intended for the collection of responses. Alpha testing is for the responses related to the product from the internal testers, and this is mostly technical and specific since it is based on whether the product functions correctly as expected or whether it meets specifications. Beta testing involves the collection of the users’ responses concerning the product from external testers (actual users) who focus from more of the functionality, usability, and performance aspects. That is the main advantage of having both processes – the product is seen in both its positive and negative aspects.
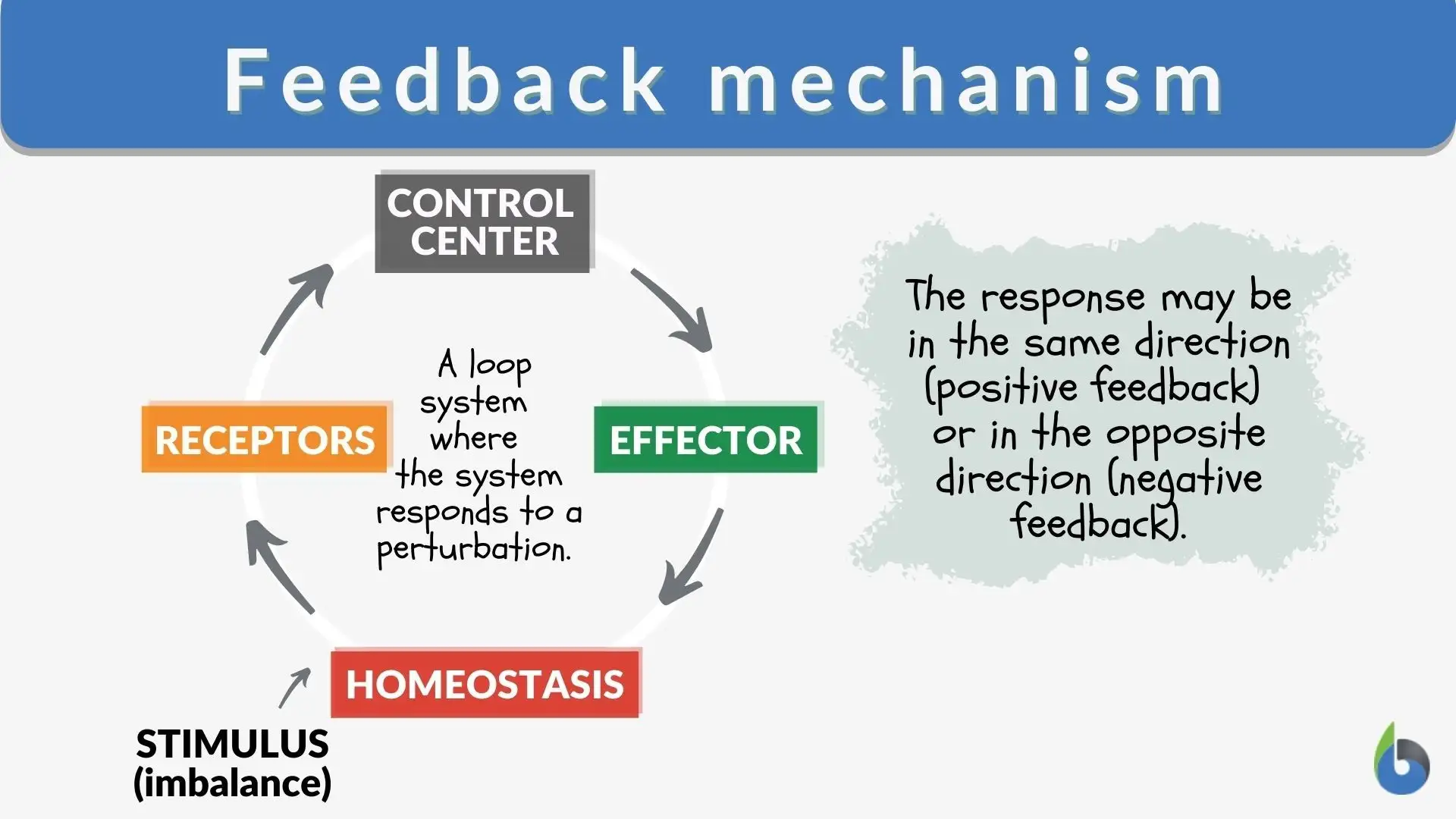
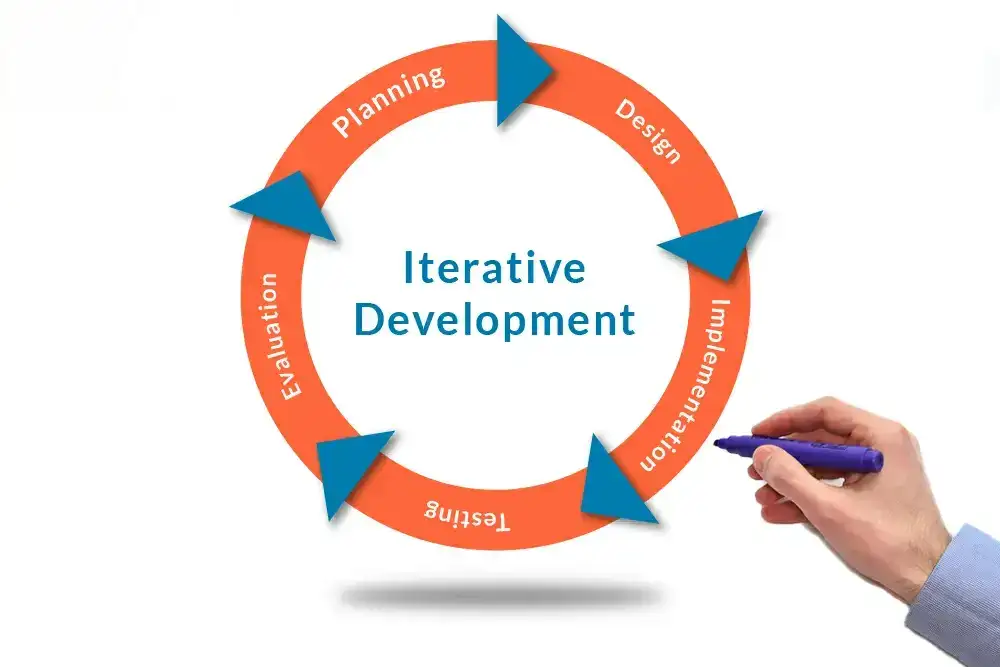
- Iterative Improvement: The iterative improvements are based on the results of alpha testing and beta testing. If bugs are detected, they must be eliminated; if there are usability issues, the product design must be modified. This is an important process of continuous improvement that culminates in a polished product.
- Forms of Acceptance Testing: Acceptance Testing involves both alpha tests and beta tests. Both are crucial procedures that attempt to determine how an application and its features behave in various conditions and according to end-user requirements.
- Contribution to Successful Software Release: In conclusion, both of the mentioned testing procedures are essential in achieving the peak of an ideal software release. A well-executed alpha test stabilizes the core product, whereas a comprehensive beta test examines the viability of the product in the market and the users’ acceptance. Both must be present, as the probability of having a poorly designed product being launched to a wider audience is much greater.
- Testing Depth and Scope: The main difference between the two test scopes is their orientation: one is directed towards the product and its features, and the other towards the product's use. In order to maximize the number of tests conducted, each of the procedures is usually executed for every possible application of the product, and every person who deals with the product is asked to give their comments and opinions. This simply implies that the purpose of both is to test as much as possible the product, covering different features and aspects. Such as, The results of the system testing are included within the alpha testing, which is to further enhance the scope of the user testing, and that is the beta testing.
If we go into topics of importance, then our main question to discuss would focus on alpha and beta testing periods in software development. Both these testing phases are the key steps because here in this process, the defect is observed, feedback is gathered, and all of these are compiled so that the best software release can be achieved.
What Should You Take Care Of If You Use Beta Test and Alpha Test
Implementing effective alpha and beta test phases requires careful planning and execution to maximize their benefits. Both processes, while distinct, demand attention to certain critical aspects to ensure a successful software release.
For Alpha Test:
- Clear Objectives: Set specific objectives for your alpha testing. Which functions or modules, if any, are you targeting? Which problems are you especially concerned with identifying at this phase? Giving internal testers a sense of purpose is beneficial.
- Comprehensive Test Cases: Create exhaustive lists of test cases that would consider all the main purposes of the system and even marginal ones. This is important to note that because internal testers are knowledgeable, they should be encouraged to do exploratory testing rather than perform testing scripts. Most of the time, this entails performing extensive system testing to confirm the integration and the entire behavior of the system.
- Robust Reporting System: Make an understandable and smooth system of reporting bugs. So that internal testers do not face any problem with logging issues, eliciting all steps required for repetition, expectation of the outcome versus the reality, and attaching pictures or files of the console. This speeds up bugfix delivery and helps testers and engineers maintain essential feedback.
- Dedicated Resources: Give enough time for all the necessary tasks to go through the alpha test and preparation phases. This includes allocating testers, development money, or development hours for quick fixes once bugs have been detected till they have been fixed, and the test environment has been deemed stable. A rushed alpha test will end up missing bugs that are critical and will hurt stages and the process that follows.

- Iterative Process: Have many iterations planned in the alpha testing phase. After finding and fixing a bug, a retention test must take place to see whether any new bugs have been introduced or whether the one previously identified has indeed been solved. From an iterative standpoint, it contributes to the stability of the formal release of the software.
For Beta Test:
- Targeted Recruitment of External Testers: Thoughtfully pick your external testers. Do aim to include your target within the wider audience who are open to effectively sharing their thoughts. More insightful judgements concerning usability and actual performance can be given if different types of external testers are involved.
- Clear Scope and Expectations: Explain to the external testers the objectives of beta testing. Point out the features that will be evaluated, the kind of responses expected, and the level of assistance they will receive. Clarify that updates, bug fixes or new features will not be made during this phase of testing.
- User-Friendly Feedback Mechanisms: Be sure to make it easy for external testers to give their feedback, report issues, and ask questions. It can be either through a dedicated feedback forum, an in-app feedback tool, or through a messaging application. If it is less complicated, chances are that external testers will be more involved in the user testing and will give feedback actively.
- Effective Data Collection and Analysis: Devise methods of gathering, interpreting, and eliminating any nonconstructive details from the responses of the people who are examining the product from outside the company. Segment the feedback by types of feedback (technical issues, suggestions, graphical interface comments) and provide levels of importance to reports, considering how significant or how many times they occur. With this, it will be clear how ideas obtained during beta testing will be refined and incorporated into the final stage of the software release.
- Incentivize Participation: Offer incentives for external testers in return for their time, effort, and cooperation. Incentives could come in the form of early access, discounts, recognition, or anything else, such as exclusive features. Enhancing the incentive will greatly increase participation and feedback quality in a beta test.
- Scalability and Performance: All this performance and speed ideally need to be considered even in the beta stage of a project. Too many systems work without any problems when testing is done by the initial team or laboratory, but too often, when used by a wider audience, the situation changes and performance flounders. This is especially true when trying to ensure that the program and its functionality will work properly when released to the users.
Wegic: Your Best Website Browser Builder
To develop and release a profitable piece of software, having a visible online presence is very important. This is true for app development firms and promising startups as well as an independent developer: A good informative site is required for engaging the wider audience and promoting goods or services. This is what Wegic offers as a great solution to how to build and maintain such websites.
The creativity behind Wegic is a new approach to the design of wealth management for web pages. Instead of focusing on graphics, this approach includes all the components of the graphics collected into one designer, developer, and manager, powered by artificial intelligence. Users simply start an intuitive conversation in order to create a run and monetize the site. One can imagine the convenient crafting of a customized full-fledged website within sixty seconds without the need for any programming knowledge. This is how ranging Wegic is, making it an awesome, on another level, tool of choice to those who would want to start their online business quickly and professionally as part of a planned software release.
Here are the steps to build a website with Wegic's AI assistant:
Step 1: Talk with AI about your requirements
Step 2: Choose your target option provided by AI
Step 3: Confirm the details of your website
Step 4: Waiting for generating, then get your own website design!
Main Features of Wegic:
- Conversational Brilliance: The new and much ingeniously defined phase of website building is created by Wegic through its conversational interface. Users communicate with Wegic through natural language, just by chatting, to express their ideas and give instructions for the creation of their website. The very name was considered a technical hurdle for website development. Hence, no technical hurdle can stand before anyone who can design the concept of his choice and put it into practice.
- Effortless Deployment: When you have already perfected your website, you are ready to publish it with Wegic just by clicking a button. Making a website with a custom web address doesn’t need any additional skills for publishing purposes, as it can be done within an instant. As such, it is particularly appealing, especially when one shares urgency in sharing their product and company information to a wider audience.
- Tailored to Perfection: Wegic drops the tools and guidance to customize the website exactly as you've envisioned it. You lay it out, you write the content, so you control every element to ensure that your website represents your brand and carries your message adequately. With such customization, your website stands.
- Adaptive Awesomeness: It is not a surprise to anyone that a website should look great on any screen and perform flawlessly on every screen in the multi-device context of today. Wegic makes it possible for websites to be their adaptively awesome, in other words, looking perfect whether one uses it on a desktop, a tablet, or even a smartphone. It is important because this level of responsiveness can allay your entire wider audience.
- AI Manager for Updates: Getting your sites in shape begets upkeep along with the actual maintenance, and here Wegic's AI Manager takes care of it for you: you never have to think of manual updates or may not even bother with anything relating to the technical maintenance of your website. All those tasks are handled by AI, which keeps your websites updated, secure, and performing optimally. Head to your core business in the meantime, maybe creating a killer software release.
- Multilingual Support: Businesses and their projects targeting the entire world in terms of their reach would make use of multilingual support from Wegic. It helps to convey messages to the wider audience in any corner of the world and so increases the chances of achieving your goals, as well as overcoming the ills of language differences.
Click the picture below to try Wegic for your own website, free of charge and time-limited!👇
Wegic empowers individuals and teams to create and manage professional websites with unprecedented ease, making it a powerful complement to any software release strategy.
Conclusion
Authoring code and conceiving it as a software product is a journey weighed by numerous layers of testing, with the alpha and beta tests acting as motivational stages in between. Where the alpha test is the deepest dive into the software’s core capabilities, understood and explained by the internal testers, beta testing assumes a similar role but to the external environment- customers in real life. The objectives of both these types of tests include uncovering any issues and soliciting constructive criticism necessary to make sure that high-quality software is released, able to win over users.
The terms beta test vs alpha test are fundamentally different in their application, with one being aimed at internal validation, which may include system testing, and the latter involves user testing and customer acceptance. However, both aim at the improvement and success of the product since no one characteristic can be viewed in disregard of the other. Most extensive testing approaches not only assess conditions but also involve interventions that maximize each and every tool available in both testing approaches and perfect the product before its public release.
While trying to grasp the intricate details of software release and focusing on quality, one must also remember that both alpha tests and beta tests are of great significance. Eventually, in order to make good use of the internet for the guidance of your customers on the latest innovations in product design, Wegic has to be brought in. Wegic, by the use of artificial intelligence, eliminates the hassle of creating and maintaining a website, enabling the creation and design of appealing and effective websites easily. It is a perfect collaboration to ensure that a software release is well-spoken, meaning it does not fail in its design and appearance, but more importantly, does not fail in reaching its audience.
You may also want to know:
Written by
Kimmy
Published on
Aug 12, 2025
Share article
Read more
Our latest blog
Webpages in a minute, powered by Wegic!
With Wegic, transform your needs into stunning, functional websites with advanced AI
Free trial with Wegic, build your site in a click!
