Iniciar sessão
Construa o seu site
How to Find Any Website’s Sitemap in 2025: 6 Free Quick Methods
Learn how to find any website's sitemap with 6 free, quick methods. Our 2025 guide helps you easily check sitemap locations for SEO and competitor analysis.

Whether you're an experienced SEO professional conducting a deep-dive competitor analysis, a web developer debugging a new site, or a business owner trying to understand your own website's architecture, knowing how to find a websites sitemap is a fundamental and indispensable skill. This knowledge acts as a key to unlocking a site's structure, revealing its content priorities, and understanding how it communicates with search engines. A sitemap is a powerful tool, and gaining access to it provides an immediate advantage in any digital strategy.
So, what is a sitemap? At its core, a sitemap is a blueprint or a detailed roadmap of a website. It is typically an XML file that lists all of a website’s important pages, videos, and other files, along with crucial metadata about each one. This file, most commonly named
sitemap.xml, isn't designed for human eyes but for search engine crawlers. Now, you might be asking, why are sitemaps important? Their significance in the digital landscape of 2025 cannot be overstated. For search engine optimization, they are vital. Sitemaps allow search engines like Google and Bing to discover and crawl all essential content on a site far more efficiently, which can lead to better, deeper, and faster indexing of your pages. This ensures that your most valuable content doesn't get overlooked. Furthermore, in the realm of competitive intelligence, learning how to find sitemap for competitor sites is like being handed their strategic content playbook. It gives you a complete, bird's-eye view of their content strategy, showing you every page they deem important enough to show a search engine. This insight allows you to identify content gaps in your own strategy and understand the topical authority your competitors are trying to build. For internal site audits, a sitemap is equally crucial. It helps you grasp the full scope of a website you're working on, ensuring no section is left un-audited or un-optimized. This article will guide you through six free and quick methods that will teach you how to find a websites sitemap, empowering you with the knowledge to analyze any website with precision and confidence.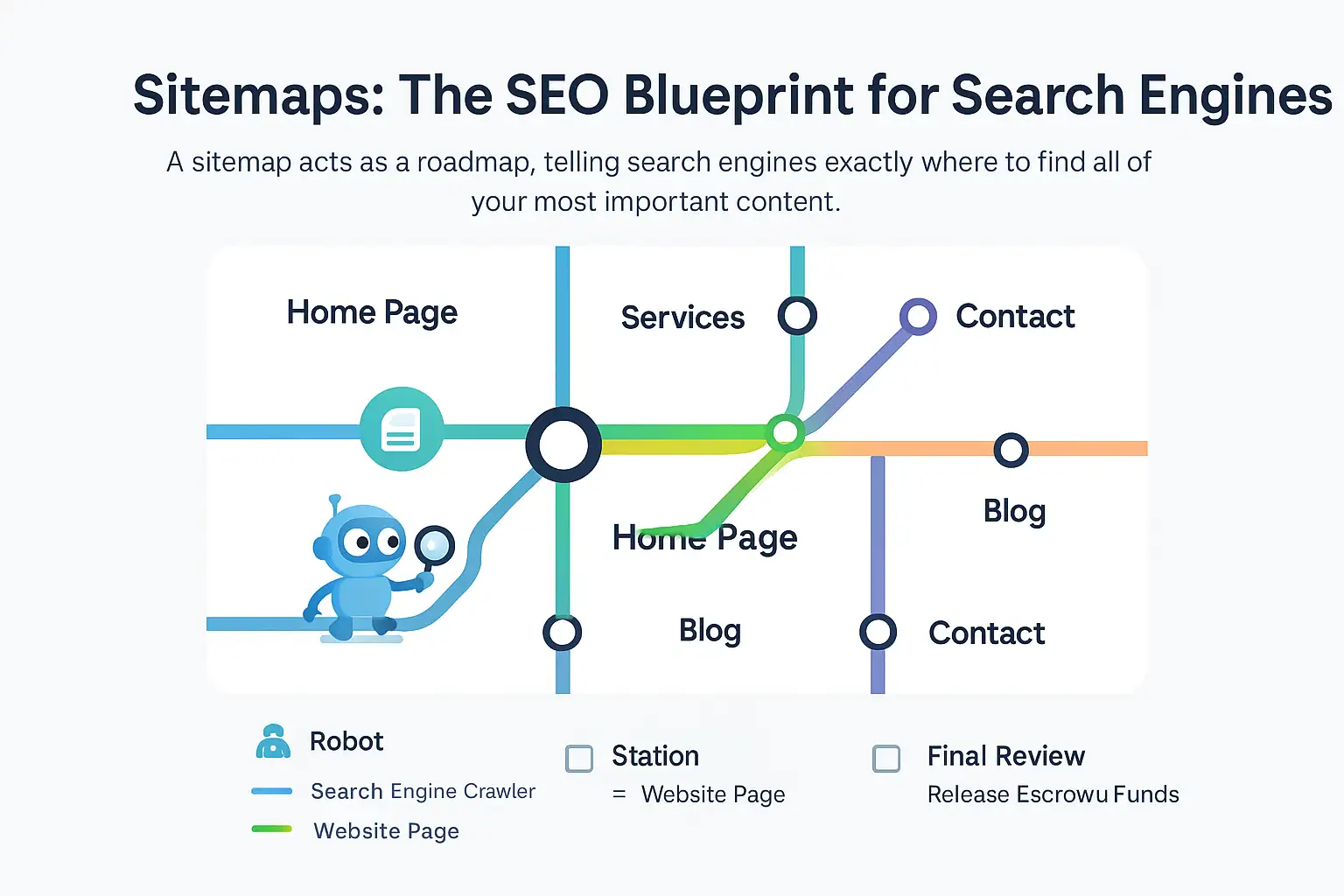
The Direct Approach: Checking Common Sitemap URLs
The first and often fastest method to find sitemap information is the direct approach: manually checking the most common URLs where sitemaps reside. This technique relies on the fact that the vast majority of Content Management Systems (CMS) and popular SEO plugins, such as Yoast SEO or Rank Math for WordPress, automatically generate sitemaps at standard, predictable locations. It's a low-effort, high-reward first step in your investigation.
The process is incredibly straightforward and requires no special tools, just your web browser.
- Open the Target Website: Navigate to the homepage of the website you wish to investigate.
- Access the Address Bar: Click on the browser's address bar where the URL is displayed.
- Test Common Filenames: Append the root domain with the following common sitemap filenames, testing each one until you find a working link. The most frequently used sitemap location is
sitemap.xml.https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml: This is the industry standard and the most likely candidate. If you find this file, it will typically list all the pages on the site or link to other, more specific sitemaps.https://www.example.com/sitemap_index.xml: This filename indicates a "sitemap of sitemaps." Large websites with thousands of pages often break their sitemaps into smaller, more manageable files (e.g., for posts, pages, products). Thesitemap_index.xmlfile acts as a master list, directing crawlers to these individual sitemaps. Finding this is a clear sign of a well-organized, large-scale website.https://www.example.com/sitemap.php: Some websites use server-side scripts to generate their sitemaps dynamically. In such cases, the sitemap might be found at a.phpextension.https://www.example.com/sitemap.txt: A less common but still valid format is a simple text file listing URLs, one per line. It lacks the metadata of an XML sitemap but serves the basic purpose of URL discovery.https://www.example.com/post-sitemap.xmlorhttps://www.example.com/page-sitemap.xml: These are very specific to WordPress sites using certain SEO plugins and represent sitemaps dedicated solely to blog posts or static pages.
When you successfully locate the sitemap xml file, your browser will display a structured page of text with a list of links. Don't be intimidated if it looks like code; you're simply looking for the list of URLs contained within the
<loc> tags. This method should always be your first line of attack due to its speed and simplicity, especially when you need to check sitemap status quickly.\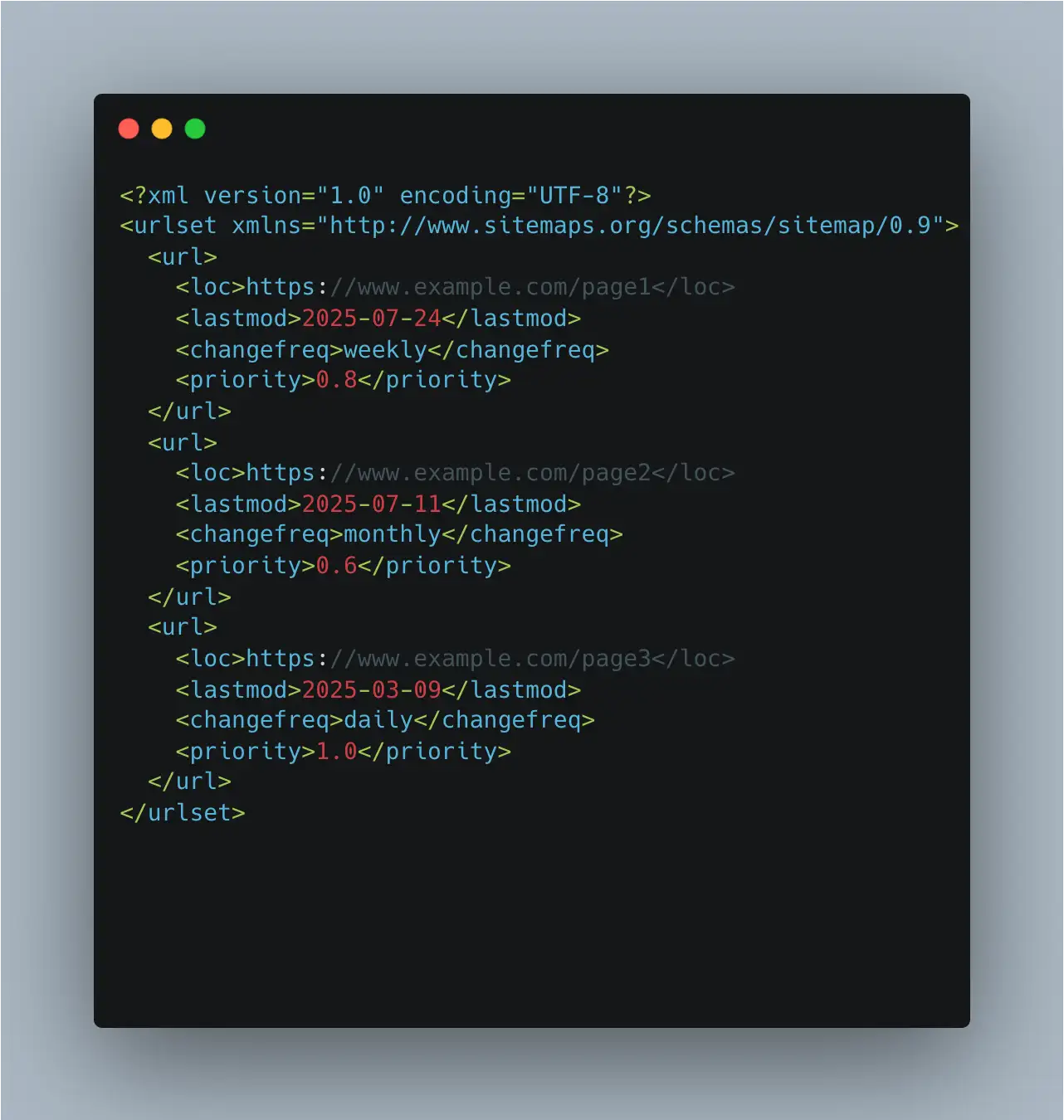
The Investigator's Clue: Finding the Sitemap Location in robots.txt
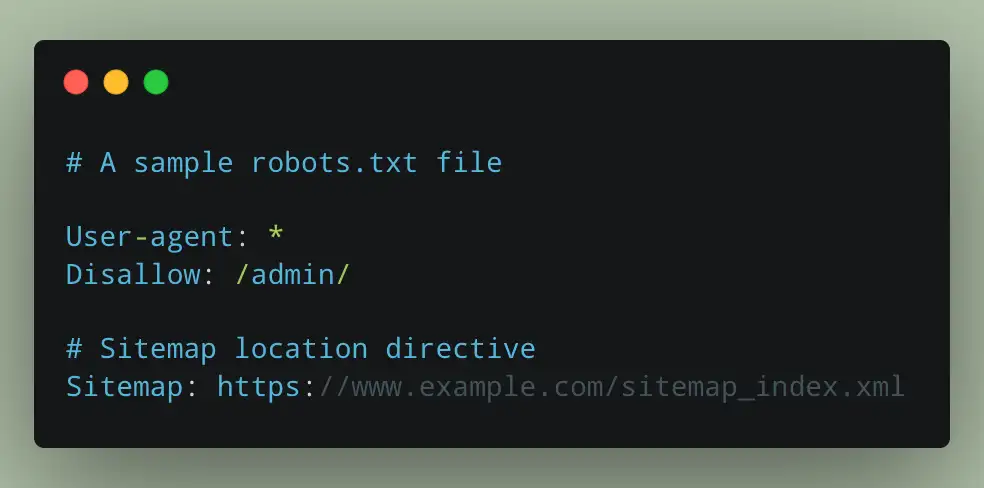
If the direct approach doesn't yield results, the next logical step is to play detective and look for clues. The most valuable clue is almost always found within the website's
robots.txt file. This file is a public-facing set of instructions for web crawlers, telling them which pages or sections of the site they should or should not crawl. As an established best practice, webmasters include a directive in this file that explicitly states the sitemap location.Finding and reading this file is just as simple as the previous method.
- Navigate to the
robots.txtFile: In your browser, go to the website's root domain and append/robots.txtto the end of the URL. For example,https://www.example.com/robots.txt. - Scan the File for the Sitemap Directive: The file will load as a plain text page in your browser. It may contain several lines of
User-agent,Allow, andDisallowcommands. Use your browser's find function (Ctrl+F on Windows, Cmd+F on Mac) and search for the word "Sitemap". - Copy the URL: The file should contain a line that looks like this:
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap_index.xml. This provides the full, direct URL to the sitemap file. You can simply copy and paste this URL into your browser to view the sitemap.
This robots.txt sitemap directive is the formal, standardized way to declare a sitemap's location to search engines. Therefore, this method is exceptionally reliable. If a website has a sitemap and follows standard SEO protocols, the link will almost certainly be here. It removes all guesswork and takes you straight to the source. This is a crucial step when you need to find sitemap for competitor sites that may use non-standard naming conventions for their sitemap files.
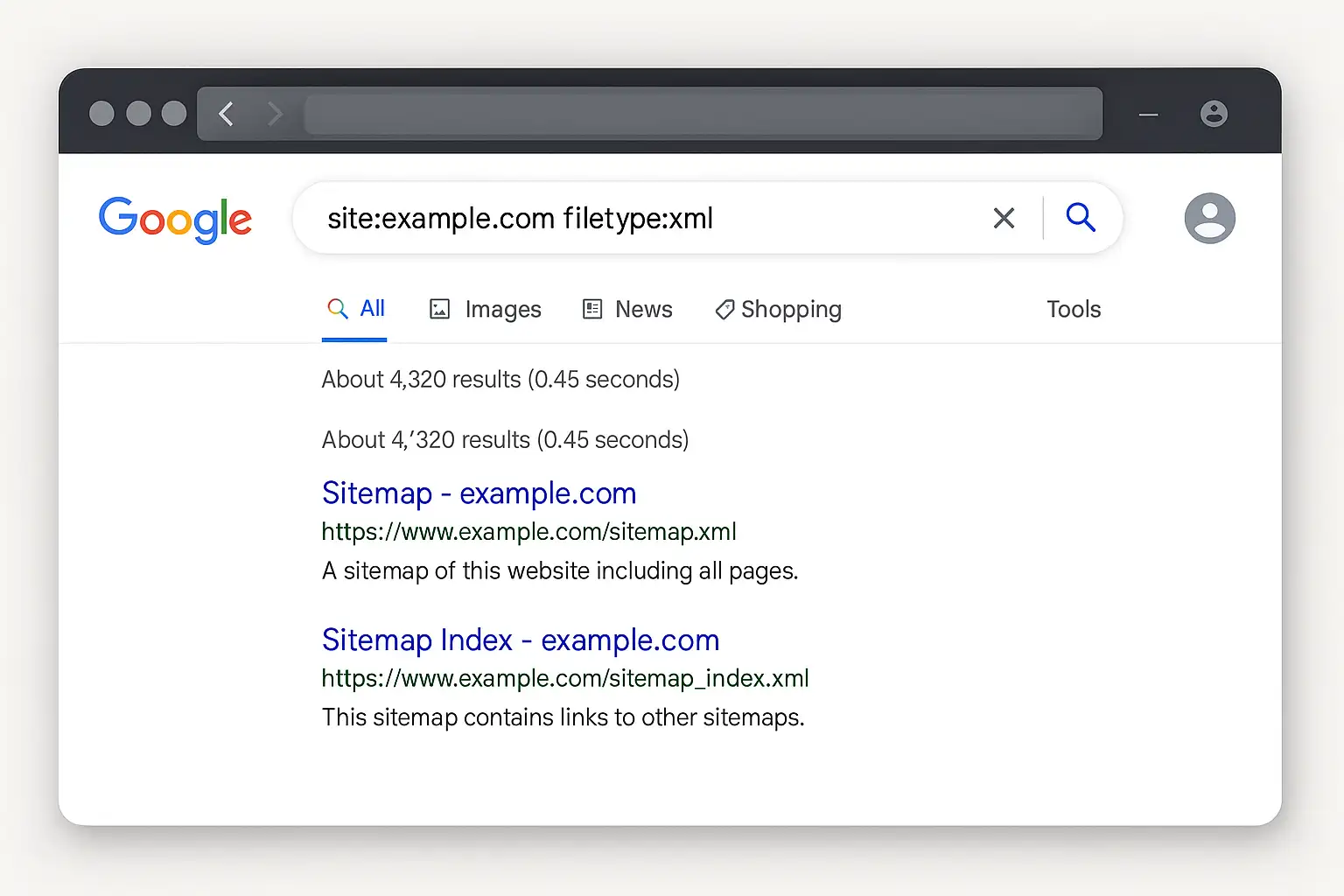
The Google Power-Up: Using Advanced Search Operators
What happens when a sitemap isn't located at a common URL and isn't declared in the
robots.txt file? It's time to leverage the immense power of Google itself. Using advanced search operators, you can ask Google to search for specific file types or URL patterns exclusively within a single domain. This technique is incredibly effective for uncovering sitemaps that have been indexed by Google but aren't publicly linked. It's a favorite tool for SEOs looking to find sitemap for competitor data.Here's how to use Google as a powerful sitemap checker:
- Go to Google Search: Open the Google homepage.
- Use Specific Search Queries: Type the following commands into the search bar, replacing
example.comwith the domain you are investigating.site:example.com filetype:xml: This is a broad but effective command. It instructs Google to return results for any XML file it has found and indexed on the specified domain. Since the most common sitemap format is XML, the sitemap file is usually the top result.site:example.com inurl:sitemap: This operator is more targeted. It tells Google to look for any URL on the target domain that contains the word "sitemap." This will catch files namedsitemap.xml,sitemap_index.xml, or even pages with URLs like/company/sitemap.site:example.com ext:xml inurl:sitemap: This is the most specific and powerful combination. It narrows the search to only show XML files that also have "sitemap" in their URL. This query filters out almost all irrelevant results and is highly likely to pinpoint the exact sitemap location.
This method is a testament to the fact that Google often knows more about a website than the website's own navigation reveals. If a sitemap exists and has been submitted to Google, these operators will almost certainly unearth it. It's a stealthy and highly effective way to check sitemap existence without ever touching the target website directly.
The Owner's Dashboard: Finding Sitemaps in Google Search Console
While the previous methods are excellent for analyzing external websites, the single most definitive way to find your own sitemap is by using Google Search Console (GSC). This free service from Google is the control center for your website's relationship with the search engine. If you have ownership or authorized access to a website's GSC property, you can find the sitemap and a wealth of diagnostic data with just a few clicks.
This method is essential for any website owner or manager.
- Log in to Google Search Console: Access your GSC account.
- Select Your Property: Choose the website you want to examine from your list of properties.
- Navigate to the Sitemaps Section: In the menu on the left-hand side, look for the "Indexing" heading. Under it, click on the "Sitemaps" link.
- View Submitted Sitemaps: This page is your Google Search Console sitemap dashboard. It will show you a list of all the sitemaps that have been submitted for this property. You will see the exact URL, the date it was last read by Google, and its status (e.g., "Success," "Couldn't fetch," or "Has errors").
The unparalleled benefit of using GSC is that it goes beyond simply helping you find sitemap data. It tells you whether Google can actually access and process your file correctly. If there are errors preventing Google from crawling your pages, GSC will identify them here, allowing you to fix the issues and ensure your site is being indexed properly. For anyone serious about their website's performance, regularly checking the Google Search Console sitemap report is a non-negotiable task.
The Automated Assistant: Using Online Sitemap Checker Tools
For those who want a quick, automated solution that combines several of the techniques mentioned above, online sitemap finders are the perfect tool. A variety of free web-based tools, often called a sitemap checker, are designed specifically to locate a website's sitemap for you. They work by running through a series of automated checks, presenting you with the result in seconds.
Using these tools is exceptionally simple:
- Find a reputable online tool: A quick search will reveal several options, such as SEO Site Checkup's sitemap finder or the tool available on XML-Sitemaps.com.
- Enter the domain: On the tool's homepage, you'll find a field where you can enter the root URL of the website you want to check.
- Run the scan: Click the "Check" or "Find" button, and the tool will get to work. It will typically check the
robots.txtfile and test a long list of common sitemap URLs automatically.
The main advantage of using a dedicated sitemap checker is speed and convenience. Instead of you manually trying ten different URLs, the tool does it for you instantly. Furthermore, many of these tools are part of larger SEO audit suites, and they may provide additional valuable data about the website's SEO health alongside the sitemap location. They are an excellent option for quick spot-checks or when you're in a hurry to check sitemap details.
The Old-Fashioned Way: Checking the Footer and HTML Sitemap
Our final method takes us back to the basics of website navigation. While the sitemap xml file is built for search engines, many websites also maintain an HTML sitemap designed for human visitors. This is essentially a single page that provides a structured, organized list of all the major pages and sections of the site, making it easier for users to find what they're looking for. Often, a link to this page can be found in the website's footer.
Here's how to distinguish between the two and use this method effectively. An HTML vs XML sitemapcomparison is simple: XML is for bots, HTML is for humans. The XML file is code, while the HTML sitemap looks like a regular webpage with a list of clickable links.
- Scroll to the Website Footer: Navigate to the homepage of the target site and scroll all the way to the bottom, into the footer section.
- Look for a Sitemap Link: Scan the links in the footer. Look for anchor text such as "Sitemap," "Site Map," or "Site Index."
- Explore the HTML Sitemap: Clicking this link will take you to the HTML sitemap. From here, you can get a great overview of the site's architecture.
While this page is designed for users, it can sometimes contain a link to the sitemap xml file for transparency or for developers' convenience. Even if it doesn't, reviewing the HTML sitemap is a valuable part of understanding how a site is structured and what content its creators want to make easily accessible to their audience. This can be an insightful part of any effort to find sitemap for competitor information.
[Image Placeholder: A screenshot of a website's footer area, with the "Sitemap" link clearly circled or highlighted.]
Alt text: Checking a website's footer navigation to find a link to the sitemap page.
The Future is Automated: Wegic.AI and Modern Sitemap Management
As we move further into 2025, the conversation around how to find a websites sitemap is evolving, thanks to the rise of AI-powered platforms. For businesses and individuals building new websites, the need to manually create or even search for a sitemap is becoming a thing of the past. Advanced AI website builders like Wegic.AI are revolutionizing this process by integrating technical SEO best practices directly into their core functionality.
When you create a website with Wegic.AI, the platform doesn't just help you design beautiful pages; it builds a technically sound foundation from the ground up. This includes the automatic generation of a perfectly formatted sitemap xml file. The system understands the structure of your site as you build it and keeps the sitemap updated in real-time as you add, remove, or change pages. This eliminates the risk of human error and ensures that search engines always have access to the most current version of your site's blueprint.
Furthermore, Wegic.AI automatically creates and configures the
robots.txt file, including the proper robots.txt sitemap directive from the very start. This means your new website is born search-engine-friendly, ready to be crawled and indexed efficiently. This level of automation is a game-changer, especially for small business owners or entrepreneurs who may not have deep technical SEO knowledge. It democratizes access to high-performance websites, handling complex tasks like sitemap management so users can focus on creating great content. This approach represents the future, where the answer to "what is a sitemap and how do I manage it?" is simply, "The platform handles it for me."[Image Placeholder: A high-quality stock photo of a person looking analytical while working on a laptop, representing modern SEO analysis.]
Alt text: A marketing professional performing an SEO analysis, a task simplified by tools that automate sitemap xml generation.
What If You Still Can't Find the Sitemap?
After trying all six methods, you may occasionally come across a website where the sitemap remains elusive. What does this mean, and what are your next steps? There are a few possibilities.
- The Website May Not Have One: It's important to acknowledge that not every website has a sitemap. While it's a strong SEO best practice, some very small sites, single-page sites, or older websites may have simply never created one. In this case, your best bet for understanding the site structure is to use a crawling tool like Screaming Frog to build your own map of its pages.
- It Could Be Dynamically Generated at an Obscure URL: Some complex, custom-built platforms might generate sitemaps at non-standard URLs that are not publicly linked or declared. Discovering these often requires deeper technical investigation or access to the site's backend.
- It Might Be Intentionally Hidden: In very rare cases, a site might have a sitemap but choose not to link it anywhere for proprietary reasons. In this scenario, the Google search operators are your most likely path to success, as Google may have discovered it through other means.
If your goal is to find sitemap for competitor sites and you come up empty, it can be an opportunity. Their lack of a sitemap could be an SEO weakness you can exploit by ensuring your own site's sitemap is perfectly configured and submitted.
Final Thoughts: The Blueprint to Digital Strategy
Mastering how to find a website's sitemap is more than just a technical exercise; it's about learning to read the web on a deeper level. Each method, from a simple URL check to an advanced Google query, is a tool that helps you uncover the structural foundation of any website. This "blueprint" is invaluable for crafting a winning SEO strategy, deconstructing a competitor's every move, and ensuring your own digital property is perfectly optimized for discovery.
We've explored how to check sitemap locations manually, how to find the robots.txt sitemap directive, and how to use a sitemap checker for automated results. We've also seen how to find the definitive Google Search Console sitemap for your own properties and how the principles of HTML vs XML sitemaps can guide your search. With these six methods in your arsenal, you are now equipped to find virtually any sitemap on the web. Go ahead—pick a website and see how quickly you can uncover its blueprint. The insights you gain will be well worth the search.
Ready for a Smarter Website?
Tired of manually hunting for sitemaps and worrying about technical SEO? The methods above are powerful for analyzing existing sites, but when it comes to building your own, there's a better way.
Wegic.AI builds your website with a perfectly optimized, automatically generated
sitemap.xml and robots.txt file from the very start. Stop worrying about the technical details and let AI handle the heavy lifting. Focus on your business while Wegic ensures your website is built for peak performance and seamless search engine discovery.
Escrito por
Kimmy
Publicado em
Aug 18, 2025
Partilhar artigo
Ler mais
O nosso blog mais recente
Páginas web em um minuto, impulsionadas pelo Wegic!
Com o Wegic, transforme as suas necessidades em websites deslumbrantes e funcionais com IA avançada
Teste gratuito com a Wegic, construa o seu site num clique!